38 sn1 reaction energy diagram
The S N 1 reaction energy diagram illustrates the dominant part of the substrate with respect to the reaction rate. The rate-determining step is the formation of the intermediate carbocation, or carbenium ion. Energy Diagram For Sn2. It starts with the kinetics of SN2 reaction and covers the energy diagrams including questions on activation energy, enthalpy, the order of reaction and curved. SN2 Reaction follows second order rate kinetics. It forms a product via one transition state. Transition state is the state at which it posses.
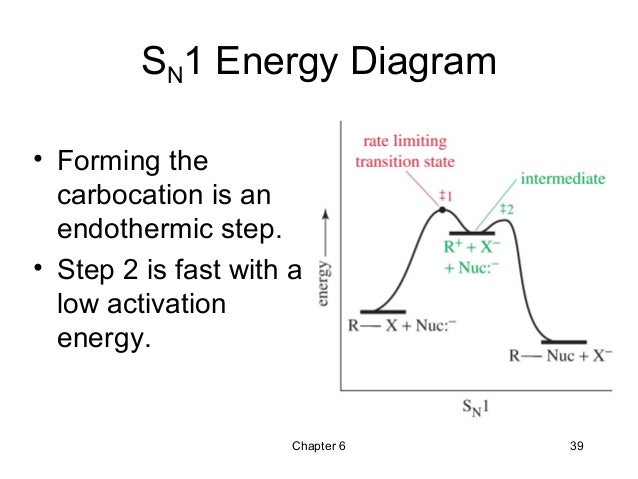
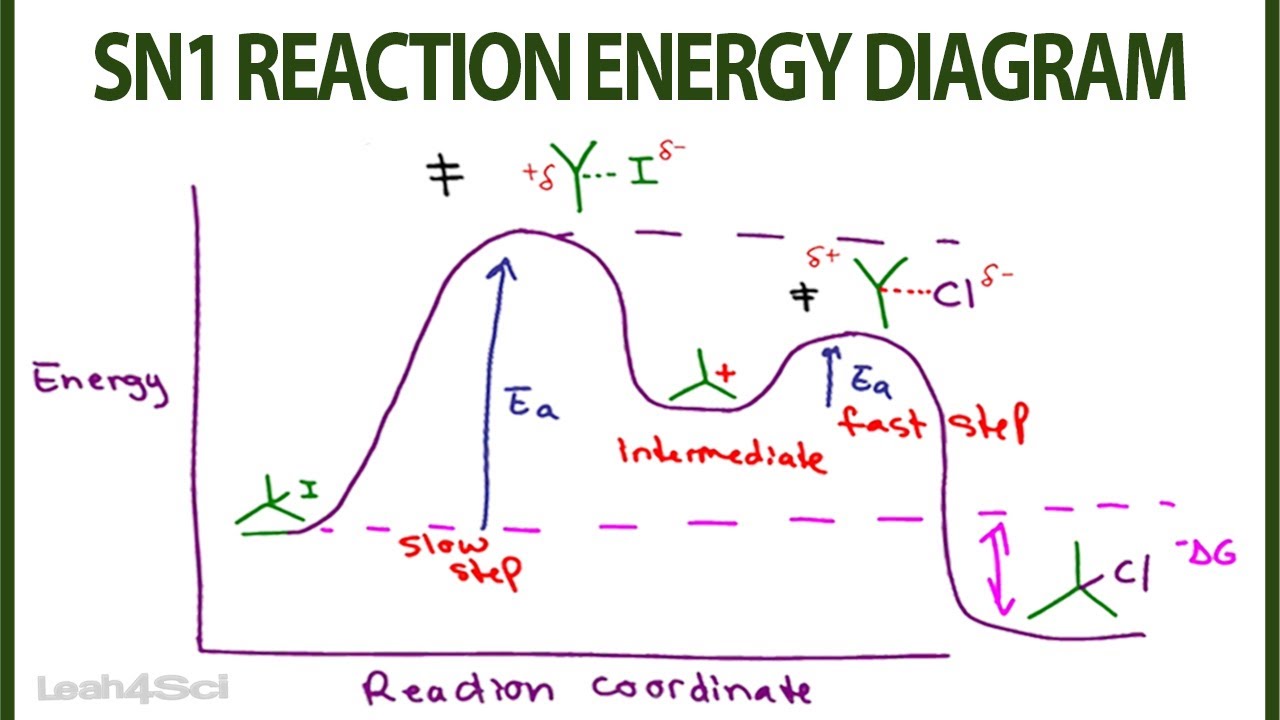
Figure 7.3 shows an energy diagram tracing the progress of a reaction that occurs by an S N 1 mechanism. The rate of the reaction reflects the activation energy required to form the carbocation intermediate. The activation energy required for step 2, addition of the nucleophile to the carbocation, is much smaller, so step 2 is very fast.
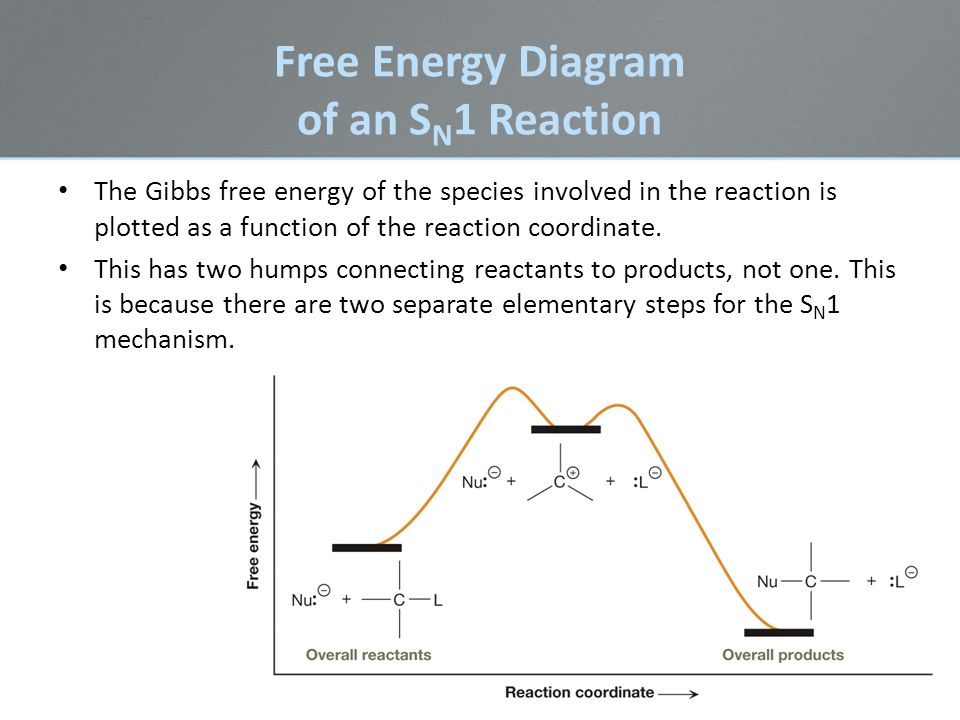
Sn1 reaction energy diagram
The S N 1 reaction energy diagram illustrates the dominant part of the substrate with respect to the reaction rate. The rate-determining step is the formation of the . Substitution Reactions (SN2 versus SN1) SN1. Elimination Reactions: E2 versus E1. Substrate: Alkene Stability Generic Reaction-Energy Diagrams. The reaction free-energy diagram in Fig. 9.11 summarizes these ideas. The first step, ion-ization of the alkyl halide to a carbocation, is the rate-limiting step and thus has the transition state of highest free energy. The rate of this step is the rate at which the alkyl halide reacts. The Atoms Chemical Kinetics Moving Charges and MagnetismMicrobes in Human Welfare Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits. Classes. Class 5. Class 6. Class 7. Class 8. Class 9. Class 10. Class 11 Commerce.
Sn1 reaction energy diagram. Potential Energy Diagram. We will be contrasting about two types of nucleophilic substitution reactions. One type is referred to as unimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN1), whereby the rate determining step is unimolecular and bimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN2), whereby the rate determining step is bimolecular. We will begin our ... The SN1 mechanism of nucleophilic substitution reactions. The rate law, energy diagram, curved-arrows, and stereochemistry with lots of practice examples. Energy Diagrams: show change in energy during a reaction. When bonds break, there is an increase in energy. When bonds form, there is a decrease in energy.a. Transition state: cannot be isolated, just a path to get somewhere. Bonds are startign to break and/or form.b. Activation energy (ΔG+): difference in energy between reactants and ... In the S N 1 reaction, the carbocation species is a reaction intermediate. A potential energy diagram for an S N 1 reaction shows that the carbocation intermediate can be visualized as a kind of valley in the path of the reaction, higher in energy than both the reactant and product but lower in energy than the two transition states.
A free energy diagram for an SN1 reaction shows one transition state. Question: A free energy diagram for an {eq}S_N1 {/eq} reaction shows one transition state. Energy level diagram for Sn1 Reaction. This graph represents that the intermediate formed is very reactive. Effect of solvent, substrste structure, and leaving group on Sn1: Effect of solvent: Rate determining step of Sn1 reaction is speed up by the effect of solvent that form carbocation intermediate. Hey All, I'm new to the forum here and a struggling O-Chem student. I'm taking OChem 1, and although I do enjoy it, I'm still timid about my answers. I'm doing a test review problems, and I was wondering if I could get some help to verify my answers. I'm not hundred percent sure, and any inputs would be greatly appreciated. Anything that isn't clear, too vague, etc. Thank you in advance! :) (**4**). Explain why free radical halogenation produces racemic mixtures of products. -Because the ra... 7.4 SN1 Reaction Mechanism, Energy Diagram and Stereochemistry. The reaction between tert -butylbromide and water proceeds via the SN1 mechanism. Unlike S N 2 that is a single-step reaction, S N 1 reaction involves multiple steps. Reaction: (CH 3) 3 CBr + H 2 O → (CH 3) 3 COH + HBr. In step 1, C—Br bond breaks and Br departs with the ...
http://Leah4sci.com/substitution-elimination presents: SN1 Reaction Energy Diagram Need help with Orgo? Download my free guide '10 Secrets to Acing Organic C... Hey All, I'm new to the forum here and a struggling O-Chem student. I'm taking OChem 1, and although I do enjoy it, I'm still timid about my answers. I'm doing a test review problems, and I was wondering if I could get some help to verify my answers. I'm not hundred percent sure, and any inputs would be greatly appreciated. Anything that isn't clear, too vague, etc. Thank you in advance! :) (**4**). Explain why free radical halogenation produces racemic mixtures of products. -Because the ra... A potential energy diagram for an SN1 reaction shows that the carbocation intermediate can be visualized as a kind of “mountain valley” in the path of the ... A chemical reaction cannot proceed more rapidly than its own slowest individual step. The individual step with the highest activation energy is the slowest one. The activation energy is the energy difference between the starting products and the transition state of the individual step. This is illustrated in the reaction energy diagrams below.
23 May 2021 — A potential energy diagram for an S N1 reaction shows that the carbocation intermediate can be visualized as a kind of valley in the path of the ...The S N1 mechanism with Ste...The SN1 Reaction Energy Dia...SN1 Reaction Kinetics1 of 3As mentioned earlier, There are two possible mechanism for how an alkyl halide can undergo nucleophilic substitution, SN2 and SN1. The SN2 reaction takes place in a single step with bond-forming and b...Continue on chem.libretexts.org »2 of 3The S N1 reaction is an example of a two-step reaction with a reaction intermediate. Evaluating reactive intermediates is a very important skill in the study of organic reaction mechanisms. Many impor...Continue on chem.libretexts.org »3 of 3In the first step of an SN1 mechanism, two charged species are formed from a neutral molecule. This step is much the slower of the two steps, and is therefore rate-determining. In the reaction energy ...Continue on chem.libretexts.org »
Energy Diagram for SN1 Reaction Definition. 1 involve only one reactant species in the rate-determining step. The analysis of the energy diagram for. 1 reaction shows that the reaction is comprised of two steps which contain two high energy unstable transition states and one stable intermediate.
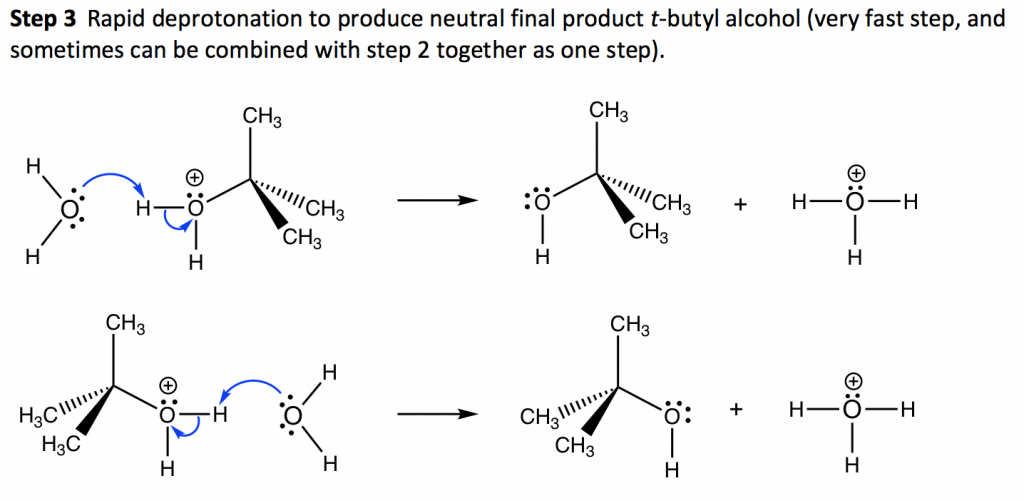
In the second step of the SN1 reaction mechanism, the carbocation is attacked by the nucleophile. Since water is used as a solvent, an oxonium ion intermediate is formed. Since the solvent is of a neutral nature, a third step where deprotonation occurs is necessary. Step 3.
SN2 reaction coordinate diagram. In this diagram, there are really only three parts: the reagents, the transition state, and the products. The transition state is the point in the reaction with the highest energy level, and the difference in energy between the reagents and transition state is called the activation energy (often abbreviated as Ea).
SN1 reaction The S1 reaction is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry. or process an energy profile (or reaction coordinate diagram) is a theoretical. SN1 reaction is a two step reaction as mentioned below: 1. Leaving group leaves first being solvolysed by solvent creating a carbocation intermediate. This is.
The fast reaction of the carbocation with the nucleophile is the driving force of the S N 1 reaction since it pulls the equilibrium to the right according to the Le Châtelier's principle.. S N 1 - A Two-Step Mechanism. Let's break down all the steps in the following S N 1 reaction looking at the energy diagram:. Step [1] Breaking the C - LG bond. In this rate-determining step, a ...
I'm currently learning about SN2/SN1 reactions. Please have patience, I haven't touched chemistry in 2 years, and this course is for a degree requirement, so I might make some incorrect assumptions about orbitals. Also, I've got quite a few questions, so maybe I'll label them with lowercase letters. > The carbocation [in the first SN1 intermediate] is sp2 hybridized and planar; it has an empty p orbital. This is what our course notes state for SN1 reactions; I'm a bit confused on this. Here...

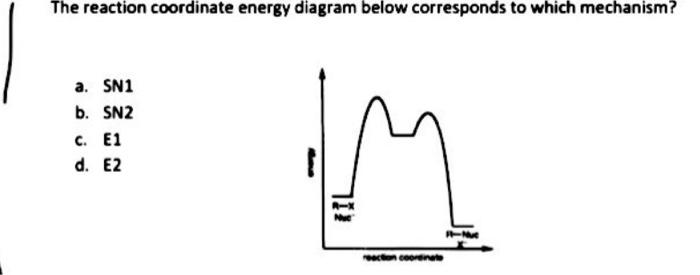
L Lu Comistry 2 Questions A28 A29 Refer To The Following Reaction Energy Profile Reaction Homeworklib
The reaction energy diagram for the SN1 reaction, from starting materials through the intermediate carbocation to the final substitution product. How to iden...
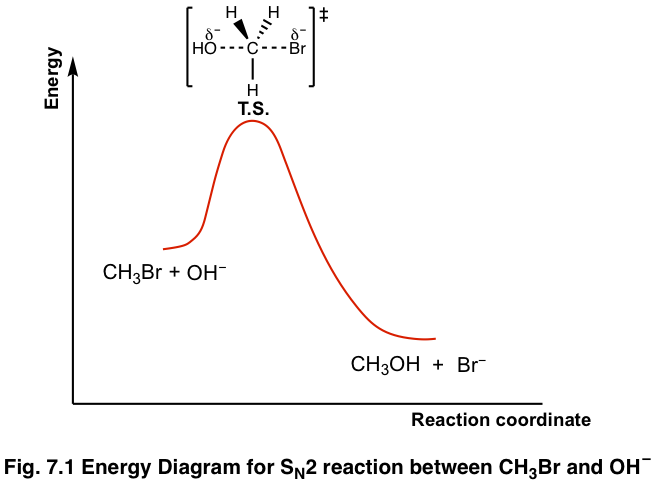
The energy changes for the above reaction can be represented in the energy diagram shown in Fig. 7.1. S N 2 is a single-step reaction, so the diagram has only one curve. The products CH 3 OH and Br - are in lower energy than the reactants CH 3 Br and OH - , indicates that the overall reaction is exothermic and the products are more stable.
I'm currently learning about SN2/SN1 reactions. Please have patience, I haven't touched chemistry in 2 years, and this course is for a degree requirement, so I might make some incorrect assumptions about orbitals. Also, I've got quite a few questions, so maybe I'll label them with lowercase letters. > The carbocation [in the first SN1 intermediate] is sp2 hybridized and planar; it has an empty p orbital. This is what our course notes state for SN1 reactions; I'm a bit confused on this. Here...
preparation of alkyl halides reaction of alcohols with reaction coordinate potential energy diagram for step 1 h cl δ. Which reaction coordinate diagram best matches the. sn1 first order nucleophilic substitution chemgapedia sn1 first order nucleophilic substitution in the first diagram a introduction sn1 reactions. Step 1.

Energy Profile Diagram Of Sn1 Reaction Chemistry Haloalkanes And Haloarenes 12711085 Meritnation Com
Energy profile diagram of SN 1 reaction: Stereochemistry of SN 1 reaction: In SN 1 reaction, carbocations are formed as the intermediate which are trigonal and planar. Carbocation has a flat structure so that nucleophile can attack it from either side (i.e. front or back) resulting in the formation of two products, one with retention of ...
$\begingroup$ At this level of abstraction it probably is fair to speak of a rate determining step, as it is (given that it actually is SN1) probably an elementary step. In more complex reactions this approximation will break down. A particular example for this is a Diels-Alder reaction with buta-1,3-diene, where the trans conformation is lower in energy.
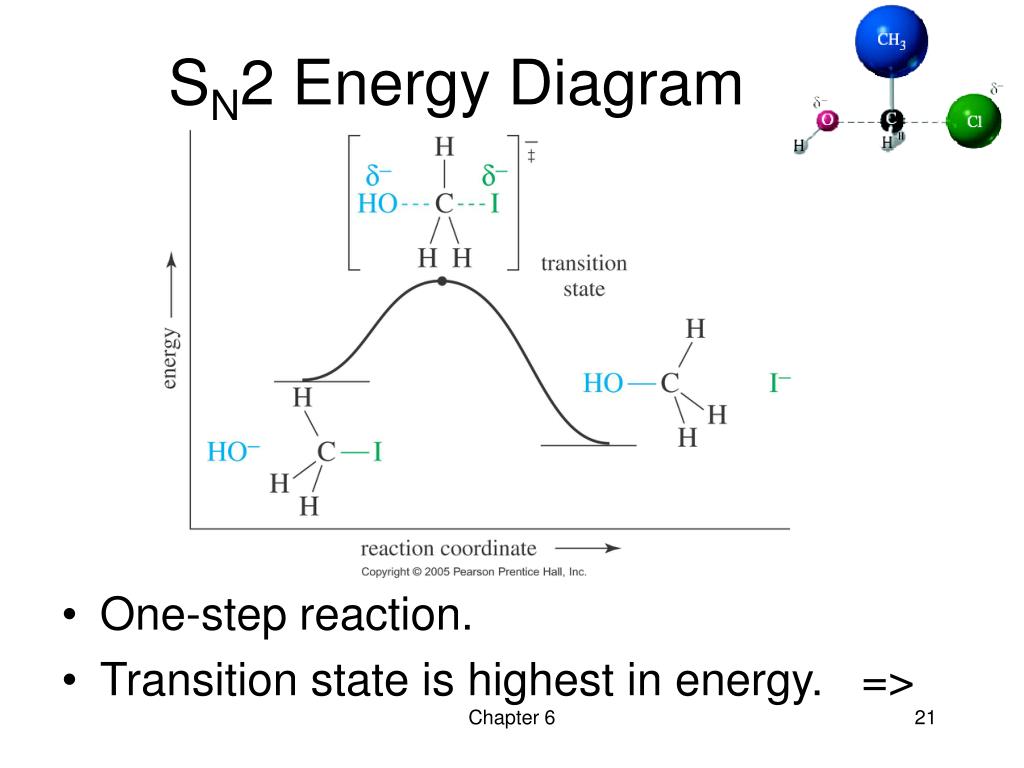
Ppt Chapter 6 Alkyl Halides Nucleophilic Substitution And Elimination Powerpoint Presentation Id 2977042
Energy diagrams SN1 and SN2. Jessica L. Santos. 699 followers . Organic Chemistry Reactions. Chemistry Help ... Sn1, Sn2, E1, E2 Orgo Reactions Handy Chart. Abigail Ameri. General Chemistry and Organic Chemistry. Chemistry Quotes. Chemistry Help. Chemistry For Kids. Chemistry Lessons. Chemistry Experiments.

Energy Diagram Of Sn1 And Sn2 Reactions The Order Of Hydrolysis Of Rx By Sn1 Is 3 O 2 O 1 O Rx And By Sn 2 Path Is 1 O 2 O 3 O Rx Which Of The Following Statements Are
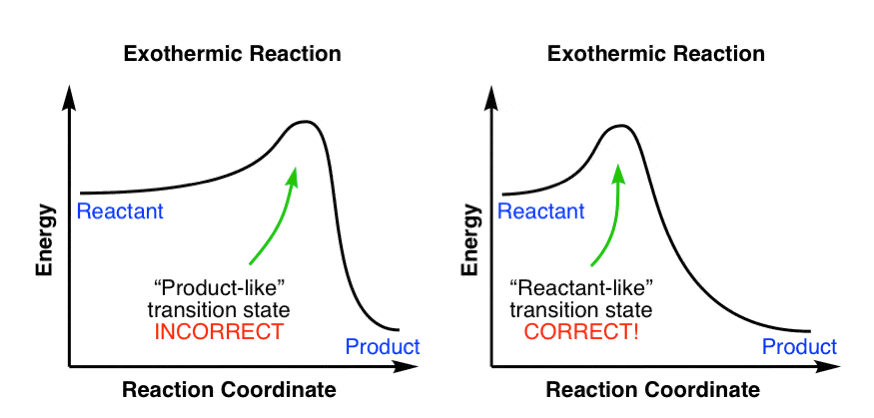
Yes, that diagram would be correct for the generic reaction. However in the specific case of an SN1 reaction the intermediate is almost always higher in energy than the reactants or the products, as they usually involve a carbocation.
Hey All, I'm new to the forum here and a struggling O-Chem student. I'm taking OChem 1, and although I do enjoy it, I'm still timid about my answers. I'm doing a test review problems, and I was wondering if I could get some help to verify my answers. I'm not hundred percent sure, and any inputs would be greatly appreciated. Anything that isn't clear, too vague, etc. Thank you in advance! :) (**4**). Explain why free radical halogenation produces racemic mixtures of products. -Because the ra...
Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram. SN1 reaction is a two step reaction as mentioned below: 1. Leaving group leaves first being solvolysed by solvent creating a carbocation intermediate. This is. whose proposed mechanism and free energy diagram are depicted Figures 1 and 2. Figure 2: Reaction coordinate diagram for an SN1 reaction1. 1.
I just need some clarification for drawing this energy diagram. I'm drawing the diagram for an SN1 reaction, and for this reaction there is a hydride shift to make the carbocation more stable. Anyways, I know that on the diagram there exists at least one valley because there is at least one intermediate. I'm not sure if I'm supposed to draw another valley, because of that shift orrrr does one valley represent the carbocation before AND after the hydride shift?
1 Reaction SN1 reactions are nucleophilic substitutions, involving a nucleophile replacing a leaving group (just like SN2). However: SN1 reactions are unimolecular: the rate of this reaction depends only on the concentration of one reactant. SN1 reactions happen in two steps: 1. The leaving group leaves, and the substrate forms a
Atoms Chemical Kinetics Moving Charges and MagnetismMicrobes in Human Welfare Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits. Classes. Class 5. Class 6. Class 7. Class 8. Class 9. Class 10. Class 11 Commerce.
The reaction free-energy diagram in Fig. 9.11 summarizes these ideas. The first step, ion-ization of the alkyl halide to a carbocation, is the rate-limiting step and thus has the transition state of highest free energy. The rate of this step is the rate at which the alkyl halide reacts. The
The S N 1 reaction energy diagram illustrates the dominant part of the substrate with respect to the reaction rate. The rate-determining step is the formation of the . Substitution Reactions (SN2 versus SN1) SN1. Elimination Reactions: E2 versus E1. Substrate: Alkene Stability Generic Reaction-Energy Diagrams.


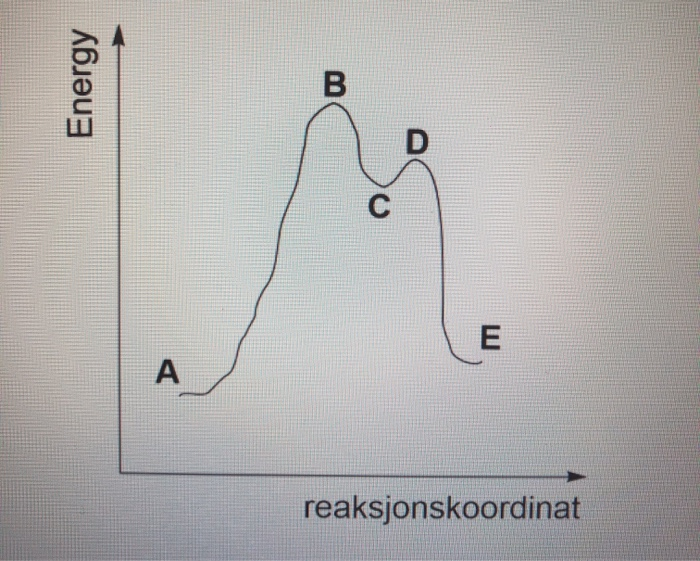
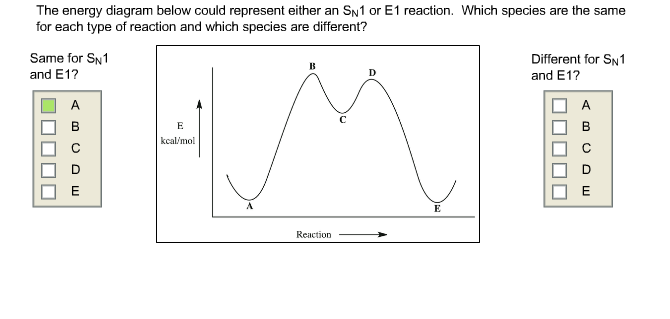












.png)


Comments
Post a Comment