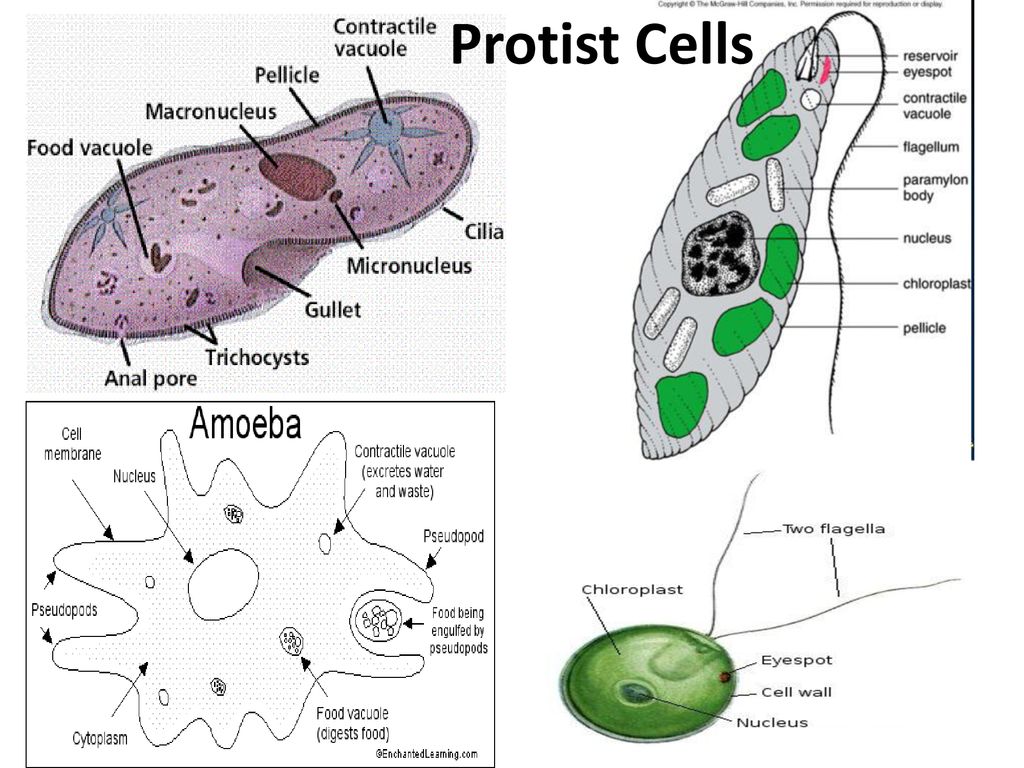
42 protist cell diagram
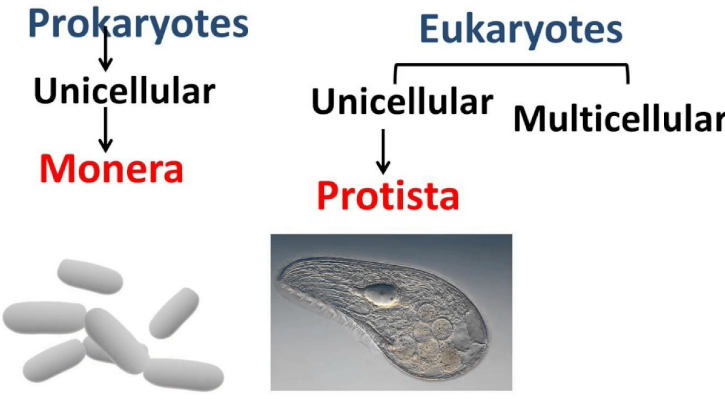
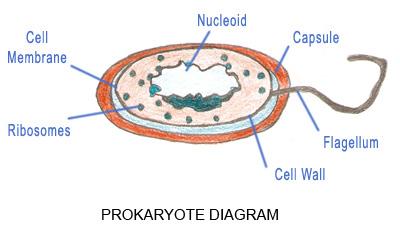
View Protist and Fungi VENN DIAGRAM.pdf from SCIENCE Bio 2382 at Western University. PROTISTS colonial cilia, flagella some don't have cell walls 200,000 identified FUNGI some unicellular chitin in Microorganism are divided into Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. Organism that do not possess nucleus and lack organelles are called prokaryotes. Eukaryotic cells are those who contains nucleus as well as the organelles. Example of prokaryotes are Archaea and Eubacteria. Eukaryotic organism examples are Algae, Fungi, Plants, Protists and Animals.
ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the two important methods of reproduction in protists. The methods are: 1. Asexual Reproduction 2. Sexual Reproduction. Method # 1. Asexual Reproduction: It involves only one parent. All the young ones produced asexually have the same genetic constitution as that of the parent and are called clones. ADVERTISEMENTS: Asexual reproduction […]

Protist cell diagram
Structure and metabolism of protists. The structure of protists is hugely variable, far more so than the rest of the eukaryotes. Protists share only a few general characteristics. A key feature of all protists are their eukaryotic cells. Because protists are eukaryotes, their cell or cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. The World of Protists. For Students 9th - 12th. For this protists worksheet, students will look at 3 diagrams showing the steps of how an amoeba finds and eats its food. Students will complete 2 short answer questions based on the diagrams. Get Free Access See Review. Cell Structure, Metabolism, and Motility. Protists are an incredibly diverse set of eukaryotes of various sizes, cell structures, metabolisms, and methods of ...
Protist cell diagram. Dec 14, 2021 · Protist Internal Structure. Because protists are eukaryotes, each protist cell contains a nucleus. This nucleus protects the protist's DNA, which is the blueprint or code that runs every function ... The cell structure of protists will be the material contained in this quiz and worksheet combo. You will be asked about the different characteristics of the cellular content in protists and how ... Cell Structure. The cells of protists are among the most elaborate of all cells. Multicellular plants, animals, and fungi are embedded among the protists in eukaryotic phylogeny. In most plants and animals and some fungi, complexity arises out of multicellularity, tissue specialization, and subsequent interaction because of these features. Although a rudimentary form of multicellularity exists among some of the organisms labelled as "protists," those that have remained unicellular show ... Protists are a diverse collection of organisms. While exceptions exist, they are primarily microscopic and unicellular, or made up of a single cell. The cells of protists are highly organized with a nucleus and specialized cellular machinery called organelles.Mar 30, 2016.
Protoctists are microscopic single-celled organisms. Some protoctists, such as Amoeba, have features like an animal cell. Others, such as Chlorella, have chloroplasts and are more like plants ... Protista Classification The kingdom Protista (in the five kingdom system) contains mostly unicellular eukaryotes. This taxonomic grouping is polyphyletic and based only on cellular structure and life styles not on any molecular evidence. Using molecular biology and detailed comparison of cell structure, scientists Protists are mainly unicellular organisms that have a complex cellular structure. In this lesson we'll learn more about the protists' cell structure, as well as some other unique features. Definition of a Protist It is a well-known fact that most bodies of water contain lots of living organisms. Ponds, lakes, and streams are inhabited by […] Cell Structure. The cells of protists are among the most elaborate of all cells. Most protists are microscopic and unicellular, but some true multicellular forms exist. A few protists live as colonies that behave in some ways as a group of free-living cells and in other ways as a multicellular organism.
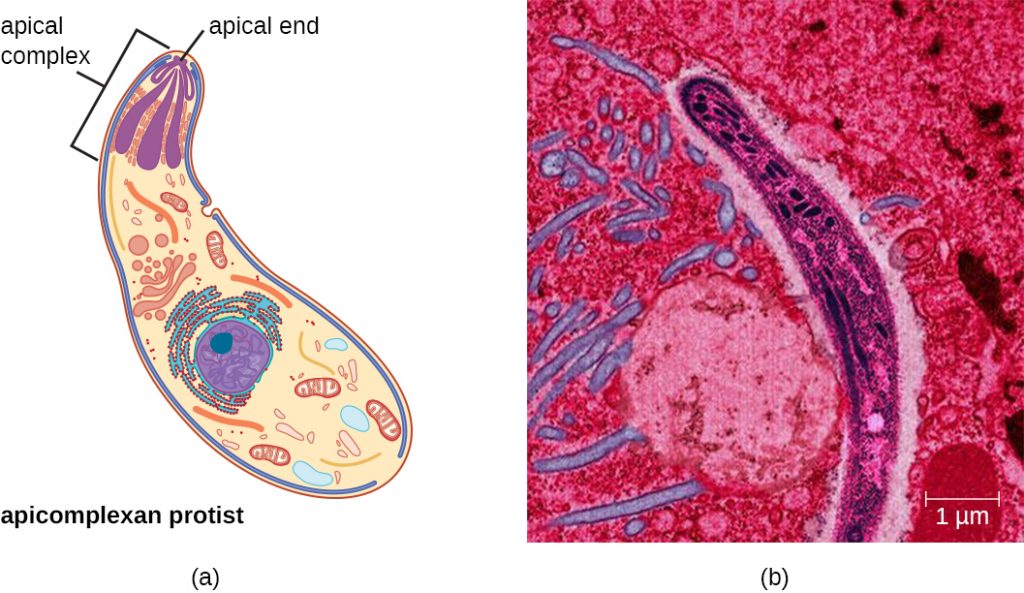
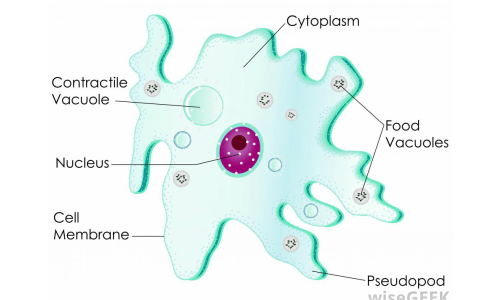
Cell Structure. The cells of protists are among the most elaborate of all cells. Most protists are microscopic and unicellular, but some true multicellular forms exist. A few protists live as colonies that behave in some ways as a group of free-living cells and in other ways as a multicellular organism. Investigation 3: The Cell Teacher Master P Teacher Master P PROTIST CELL STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS Cell structure Function Cell membrane Boundary that controls what enters and leaves the cell Contractile vacuole A membrane that stores water and expels excess water Cytoplasm Internal fluid that contains the cell structures Endoplasmic reticulum ADVERTISEMENTS: Let us learn about the top four important lineages of protists. The lineages are: 1. Euglenozoa 2. Alveolata 3. Stramenopila and Rhodophyta 4. Chlorophya. Lineages of Protists # 1. Euglenozoa: (a) Euglenoids: The Euglenoids diverged early as free-living eukaryotes and had mitochondria in their cells. They have individuals that were difficult to distinguish in […] Protist Structure. The cells of protists are among the most elaborate of all cells. Most protists are microscopic and unicellular, but some true multicellular forms exist. A few protists live as colonies that behave in some ways as a group of free-living cells and in other ways as a multicellular organism.
Apr 09, 2021 · Cell Membrane Protist Structure. Friday, April 9th 2021. | Diagram. Cell Membrane Protist. All protist cells are surrounded by a cell membrane, which is a fluid, protective layer that helps to separate the protist cell from its external environment, keeping everything inside safe and. Single protist cells range in size from less than a micrometer to thousands of square meters (giant kelp).
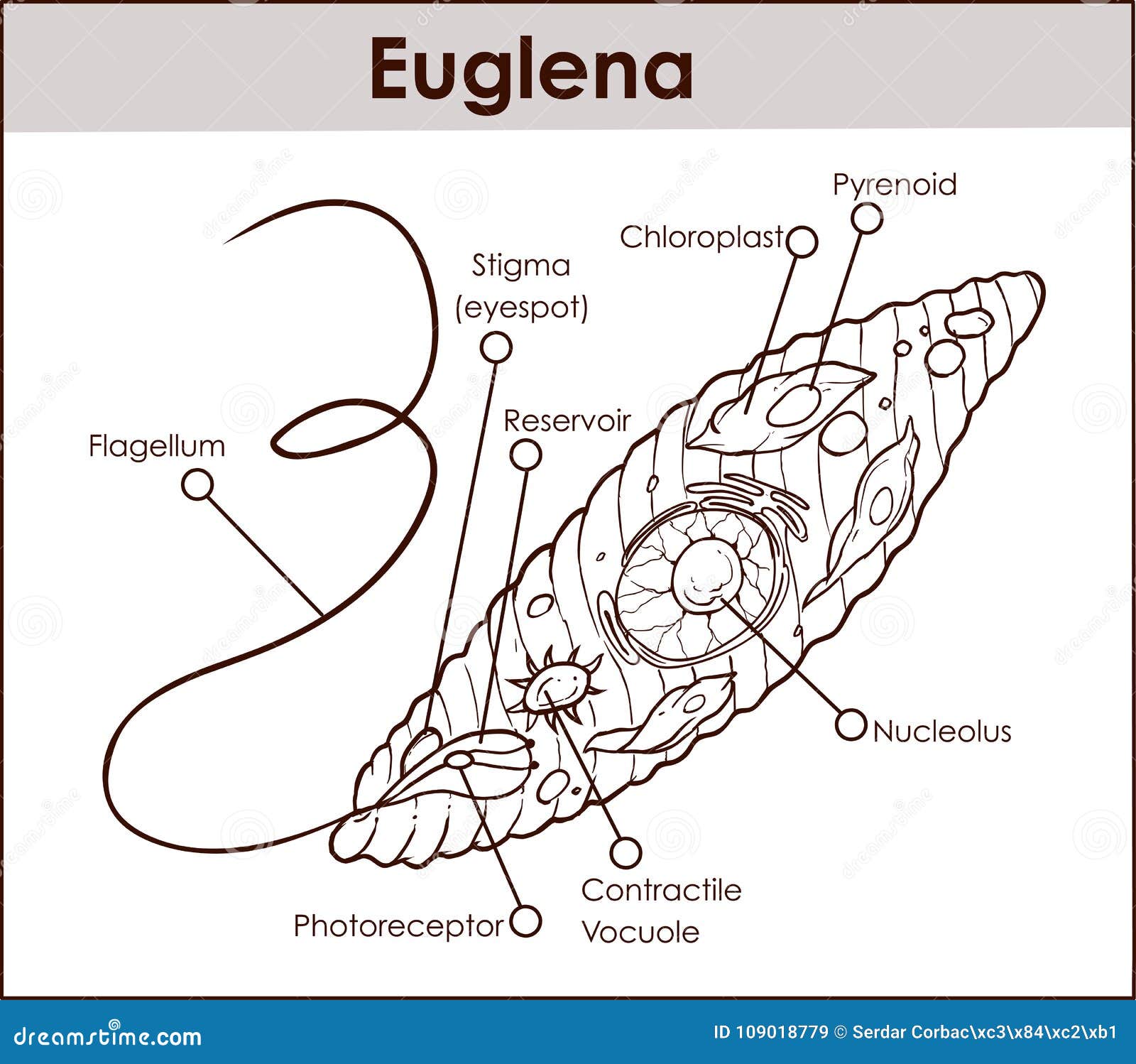
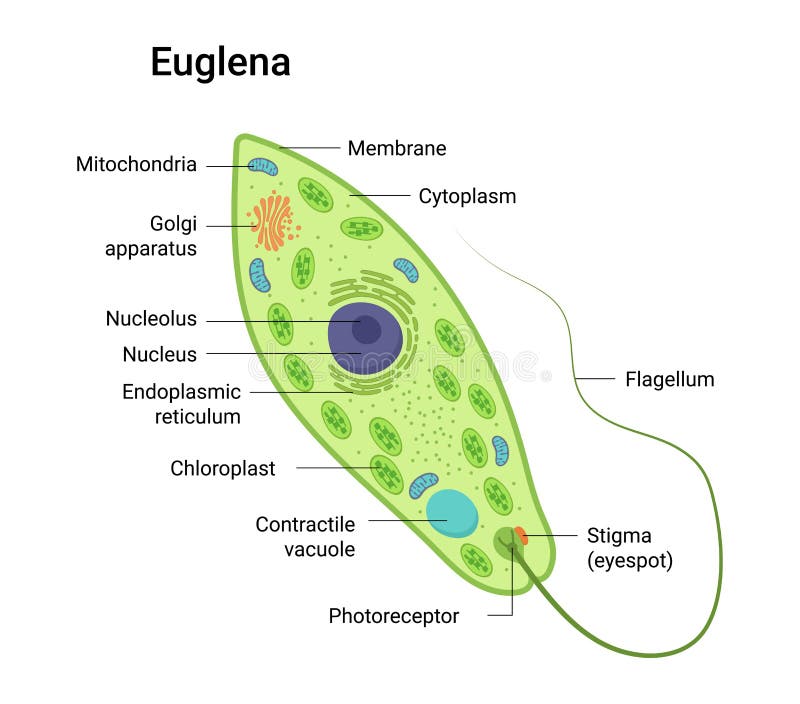
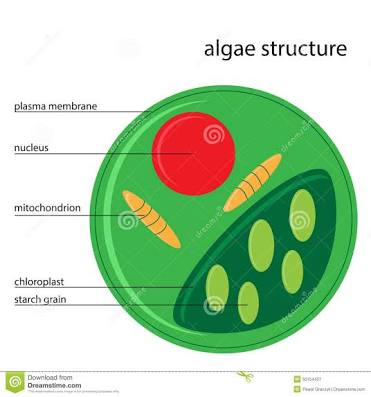
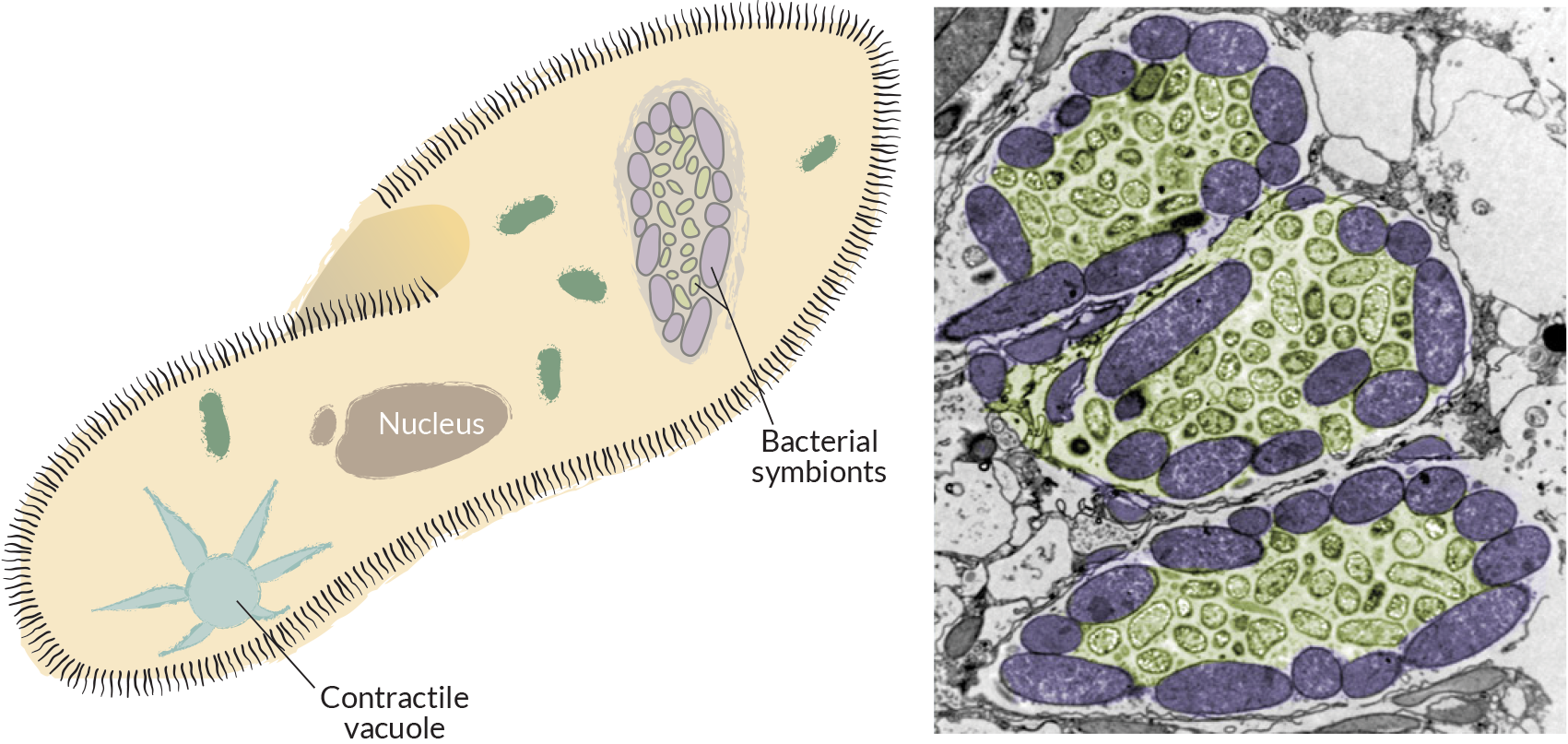
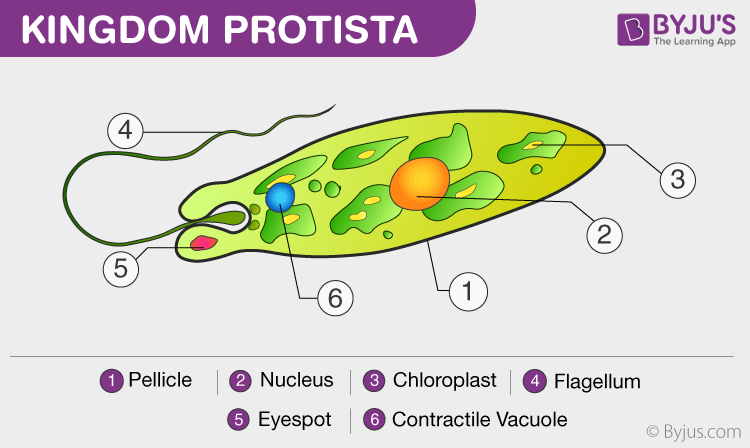
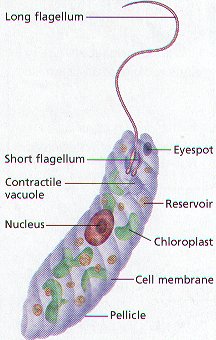
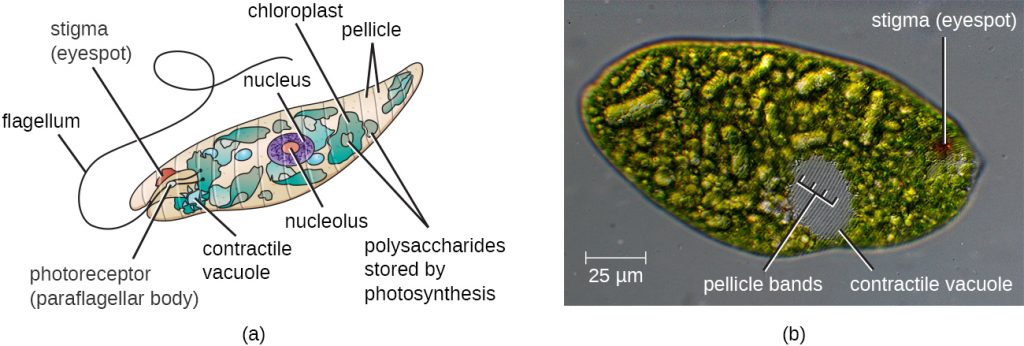
Answer (1 of 2): Protists are one-celled or multi-cellular eukaryotes that have a nucleus, ribosomes, endoplamic reticulum, golgi apparatus, and mitochondria within their cell membranes. Photosynthetic protists also have chloroplasts. Some have eyespots to detect light, and many have flagella as ...
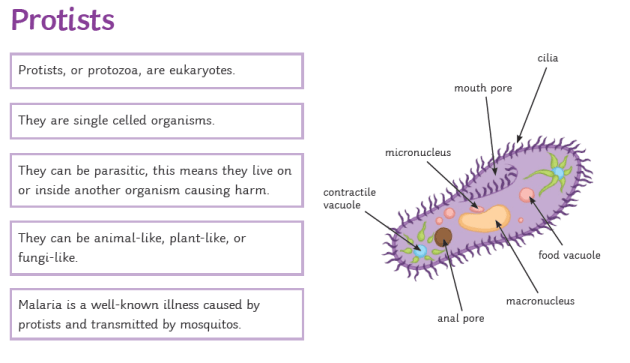
Protists is surrounded by plasma lemma (cell membrane). There may be an outer covering of pellicle, cuticle, shell or cellulose wall. It contains organelles like mitochondria, Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, 80S ribosomes, etc. They have typical 9+2 fibrils. Nucleus has typical structure—porous nuclear envelope, chromatin, nucleolus and nucleoplasm.
a common ancestral eukaryotic cell. Examine the diagram an d find where mitochondria entered into the evolutionary process. Mitochondria became part of protist cells early in the evolu-tionary proces s. Now, locate where chloroplasts entered cells. Follow the path of the arrow and you can see that algae are the only protists with
Cell Structure. The cells of protists are among the most elaborate of all cells. Multicellular plants, animals, and fungi are embedded among the protists in eukaryotic phylogeny. In most plants and animals and some fungi, complexity arises out of multicellularity, tissue specialization, and subsequent interaction because of these features ...
Protists are simple eukaryotic organisms that are neither plants nor animals or fungi. Protists are unicellular in nature but can also be found as a colony of cells. Most protists live in water, damp terrestrial environments or even as parasites. Euglena, a eukaryotic protist. The term 'Protista' is derived from the Greek word "protistos ...
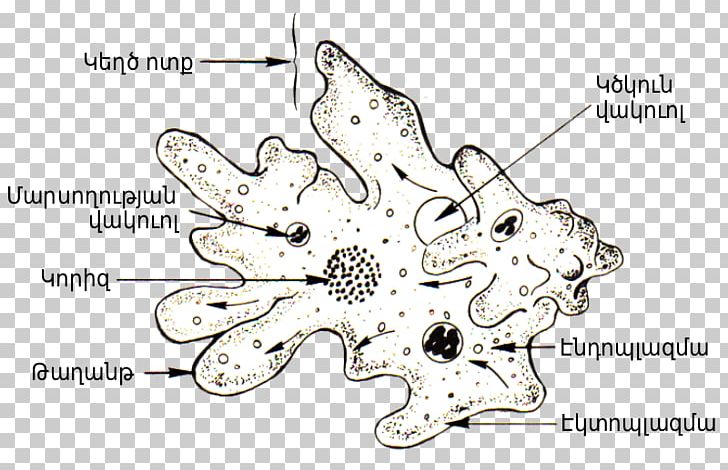
Group of aquatic and marine amoeboid protists with colorful shells composed of calcium carbonate. Has thread-like, branched pseudopods that extrude from pores in the shell. Found in tremendous numbers of oceans.
a shell-like structure on the outside of their bodies. Protist ReproductionProtists usually reproduce asexually by cell division. During cell division, the hereditary material in the nucleus is duplicated, the nucleus divides, and then the cyto-plasm usually divides. The result is two new cells that are geneti-
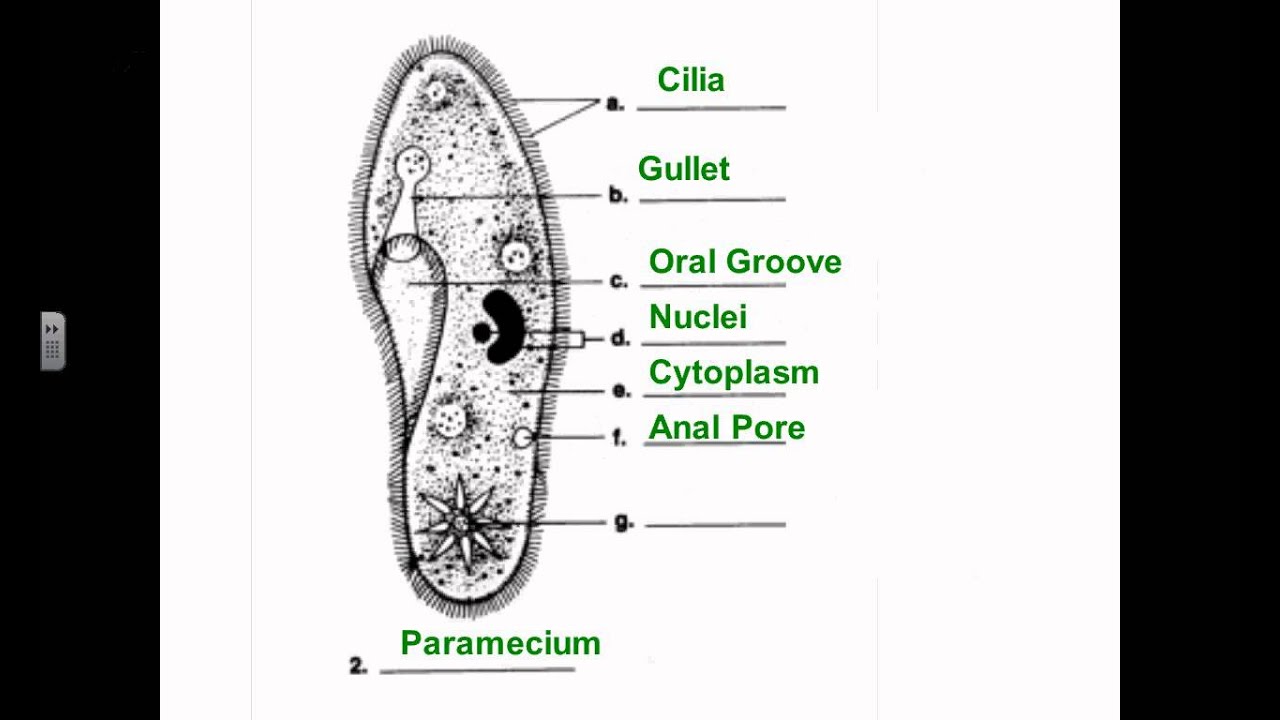
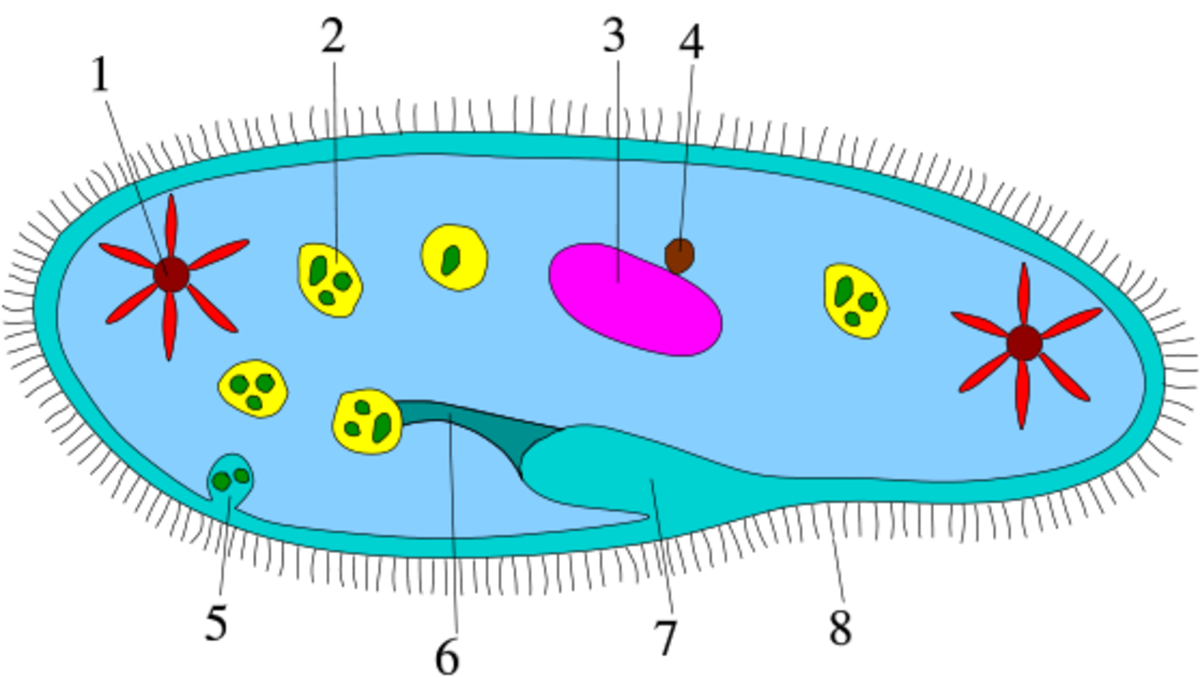
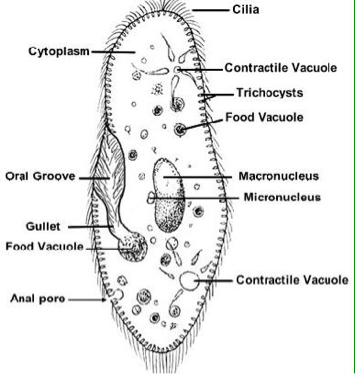
Paramecium. A single cell protist that moves and eats using cilia. It is a heterotroph. Paramecium are capable of both sexual and asexual reproduction. Amoeba. A single cell protist that moves by stretching its cytoplasm into pseudopods or false feet. Surrounds and engulfs its food. It is a heterotroph.
3 Jan 2021 — The cells of protists are among the most elaborate and diverse of all cells. Most protists are microscopic and unicellular, but some true ...
The euglena cell structure is tear-drop shaped with one end pointed and the other end, blunt (head). Organelles that are common in the animal cell and plant cell and are also found in the euglena cell structure include the Golgi apparatus , ribosomes , nucleus , endoplasmic reticulum , contractile vacuole, mitochondria , and lysosomes .
A protist (/ˈproʊtɪst/) is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus.
What is the cell structure of a protist? Protists are one-celled or multi-cellular eukaryotes that have a nucleus, ribosomes, endoplamic reticulum, golgi apparatus, and mitochondria within their cell membranes. Photosynthetic protists also have chloroplasts. Some have eyespots to detect light, and many have flagella as a means of locomotion.
Cell Structure. The cells of protists are among the most elaborate of all cells. Most protists are microscopic and unicellular, but some true multicellular forms exist. A few protists live as colonies that behave in some ways as a group of free-living cells and in other ways as a multicellular organism.
Cell Structure, Metabolism, and Motility. Protists are an incredibly diverse set of eukaryotes of various sizes, cell structures, metabolisms, and methods of ...
The World of Protists. For Students 9th - 12th. For this protists worksheet, students will look at 3 diagrams showing the steps of how an amoeba finds and eats its food. Students will complete 2 short answer questions based on the diagrams. Get Free Access See Review.
Structure and metabolism of protists. The structure of protists is hugely variable, far more so than the rest of the eukaryotes. Protists share only a few general characteristics. A key feature of all protists are their eukaryotic cells. Because protists are eukaryotes, their cell or cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles.


















Comments
Post a Comment