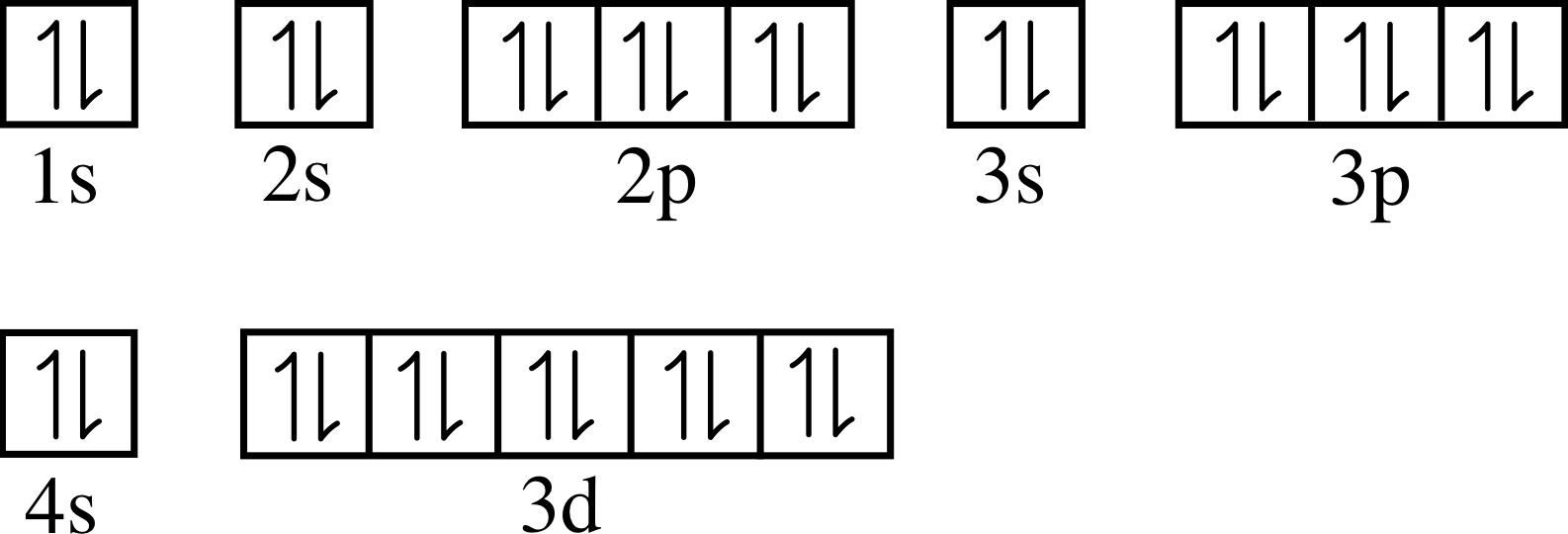
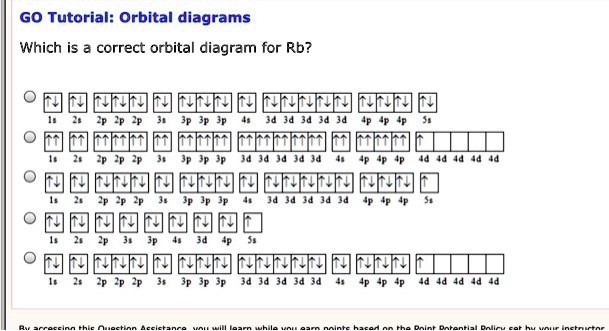
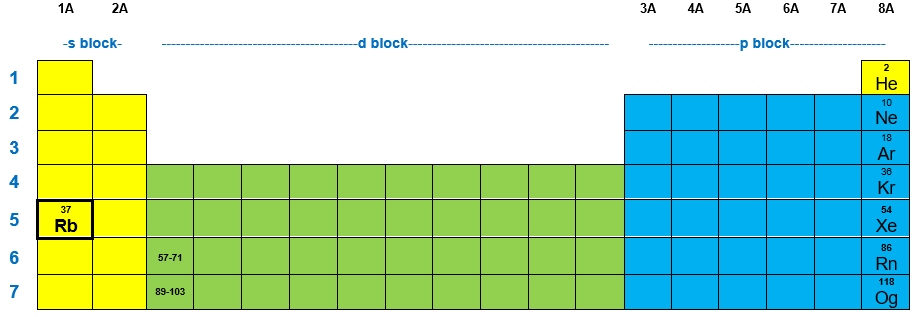
42 rubidium orbital diagram
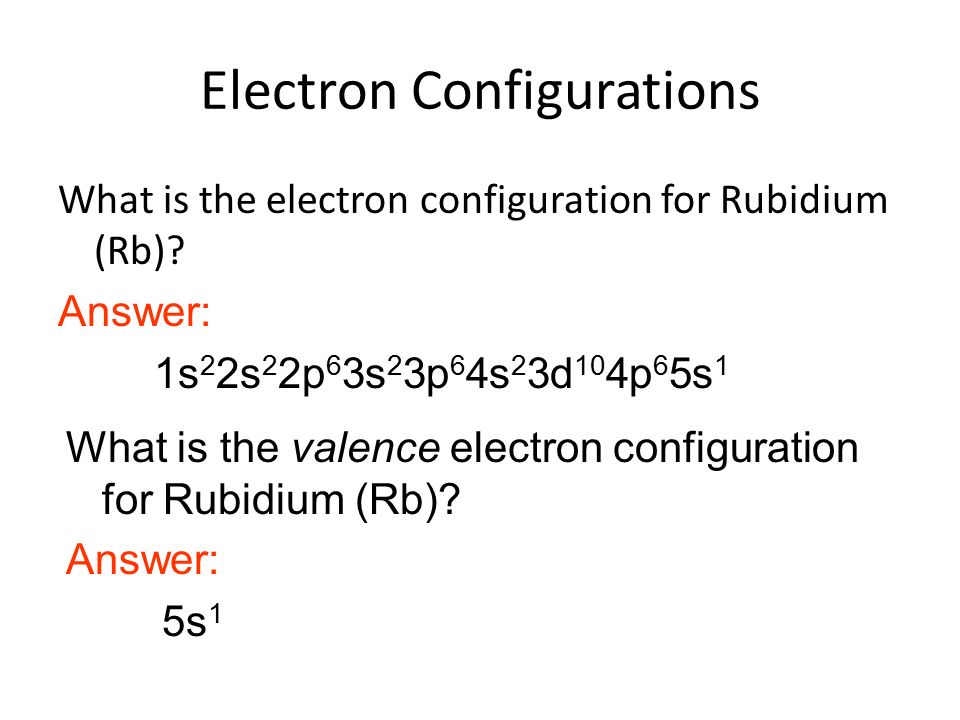
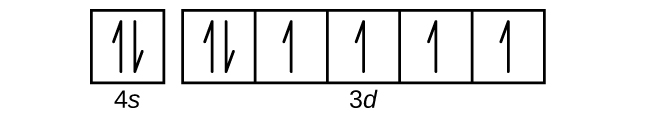
Rubidium Electronic configuration. Electronic configuration: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 6 5s 1 >> Back to key information about the elementBack to key information about the element Rubidium (Rb) has an atomic mass of Find out about its chemical and physical properties, states, energy, electrons, oxidation and more. The orbital diagram has nine boxes with two arrows in the first seven and single arrows in the last two Write the electron configuration and draw the orbital notation for atoms of oxygen and sulfur.
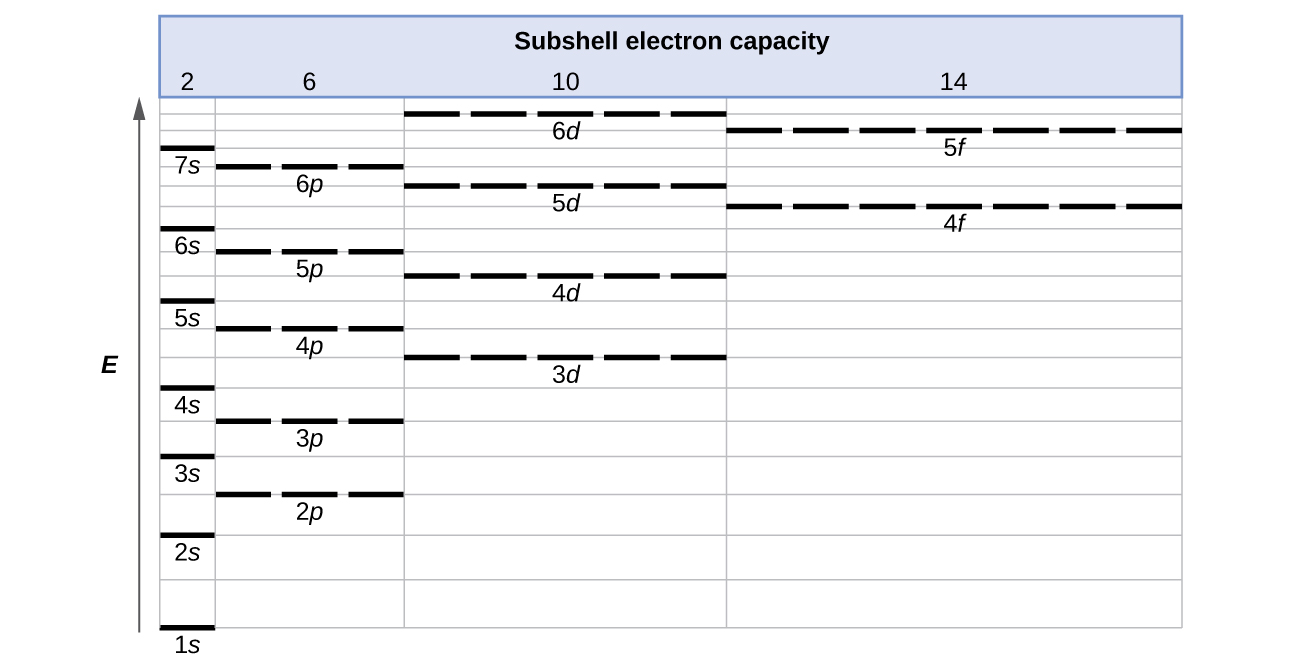
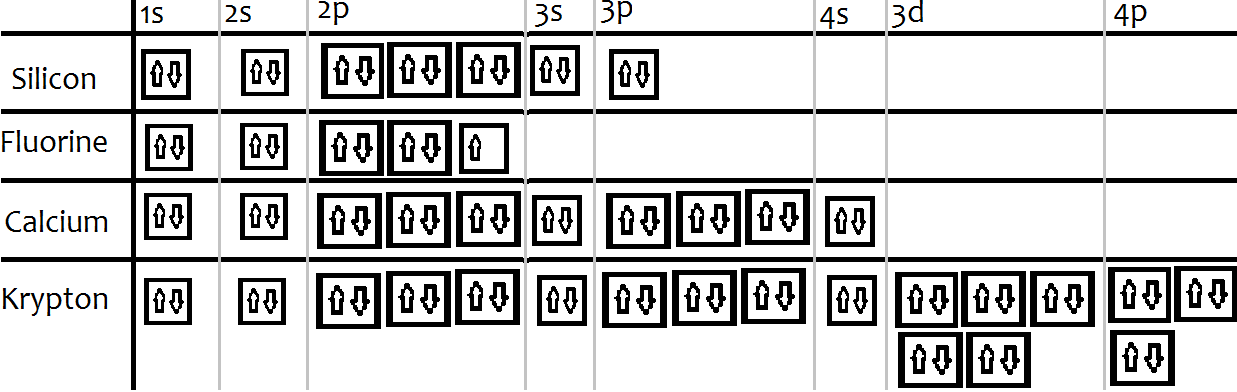
• Electron configurations are shorthand for orbital diagrams. The electrons are not shown in specific orbitals nor are they shown with their specific spins. • Draw the orbital diagram of oxygen: • The electron configuration should be: 1s 22s 22p 4 • Manganese 1s 22s 22p 63s 23p 64s 23d 5 • Rubidium 1s 22s 22p 63s 23p 64s 23d 10 4p 65s ...

Rubidium orbital diagram
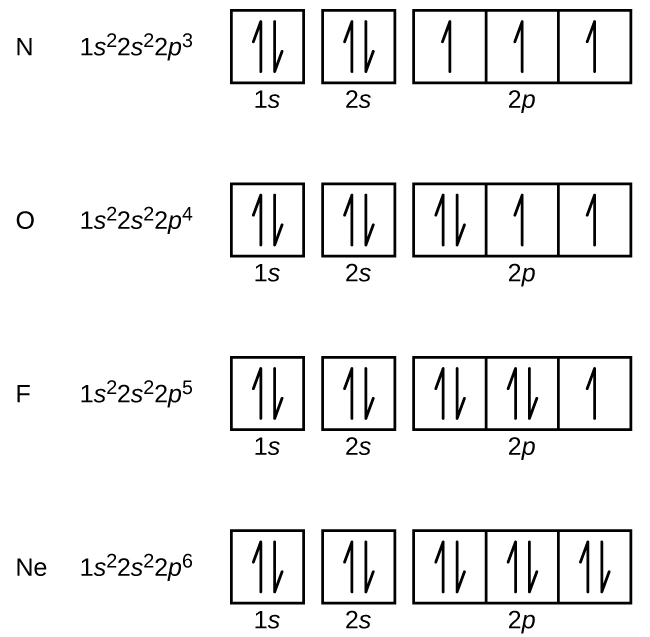
Draw the orbital diagram for the following elements: Oxygen (O) Titanium (Ti) Silicon (Si) Copper (Cu) For each of the following elements, identify if the electron configuration is correct or incorrect. If it is incorrect, give the fix to the configuration. Carbon (C) = 1s22s22p2. Sulfur (S) = 1s22s22p63p6 Orbital diagram of Rubidium (Rb) 38: Orbital diagram of Strontium (Sr) 39: Orbital diagram of Yttrium (Y) 40: Orbital diagram of Zirconium (Zr) 41: Orbital diagram of Niobium (Nb) 42: Orbital diagram of Molybdenum (Mo) 43: Orbital diagram of Technetium (Tc) 44: Orbital diagram of Ruthenium (Ru) 45: Rubidium is an element (atomic number 37). What is the correct orbital diagram would be for the element nickel? Before you can make a diagram, you will need to know the atomic number. With the...
Rubidium orbital diagram. Rubidium 87 D Line Data Daniel A. Steck Theoretical Division (T-8), MS B285 Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 87545 25 September 2001 (revision 1.6, 14 October 2003) 1 Introduction In this reference we present many of the physical and optical properties of 87Rb that are relevant to various quantum optics experiments. 9) The full electronic configuration of a rubidium atom in the ground state is 37Rb85.46 : 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s1 The last subshell of Rb is 5s and thu …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: 9. Give the full electron configuration of a rubidium atom in the ground state. Provide the orbital diagram of the last subshell ... Rubidium (Rb) orbital diagram 1s is the closest and lowest energy orbital to the nucleus. Therefore, the electron will first enter the 1s orbital. According to Hund's principle, the first electron will enter in the clockwise direction and the next electron will enter the 1s orbital in the anti-clockwise direction. Arsenic Electron Configuration - 9 images - rubidium electron configuration rb with orbital diagram, arsenic properties and occurrence assignment point,
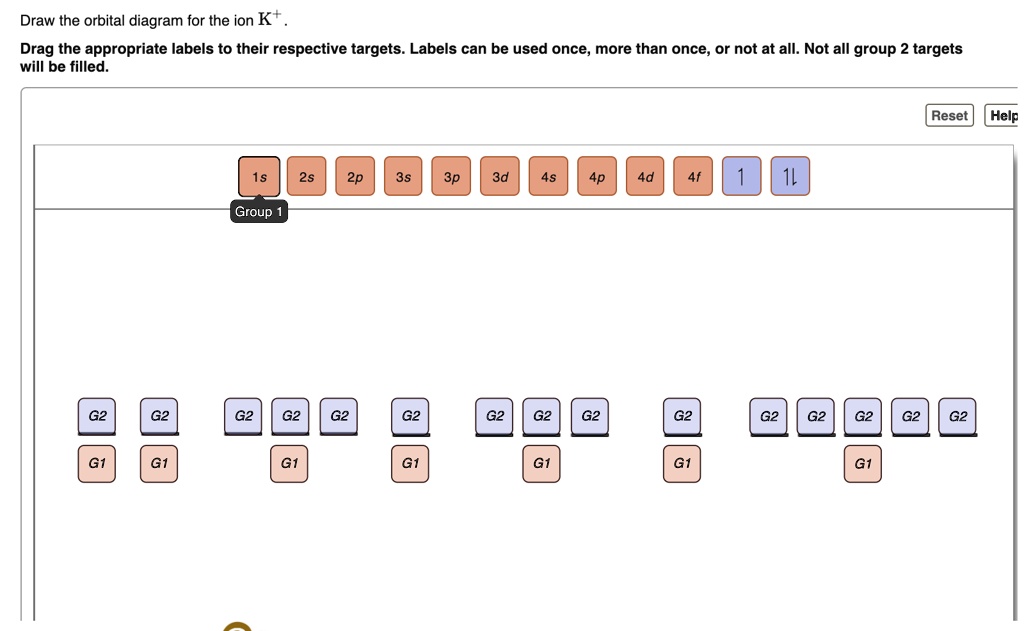
Find step-by-step Chemistry solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: Write the electron configuration and give the orbital diagram of a rubidium (Rb) atom $(Z=37)$.. transition. To understand the energy levels of rubidium, we need to consider the interaction between the electron and the nucleus and between both and an external magnetic field. The angular momentum of the valence electron is given by J = L+S (1:) where L is the orbital angular momentum and S is the spin angular momentum. To get the total angular (2 pts) Write the full e- configuration for the rubidium ion, Rb : 3. (2 pts) Draw the full orbital diagram for the aluminum atom, AI: 4. (2 pts) Draw the condensed orbital diagram for arsenic, As: 5. Answer to: Write the electron configuration, orbital filling diagram, and determine the number of valence electrons for the Rb. What is similar to...1 answer · Top answer: Rubidium has 37 electrons so its electronic configuration is equal to 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s11s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s1 and its...
(2 pts) Write the full e- configuration for the rubidium ion, Rb : 3. (2 pts) Draw the full orbital diagram for the aluminum atom, AI: 4. (2 pts) Draw the condensed orbital diagram for arsenic, As: 5. The electron configuration of lithium shows that lithium has an electron in the last orbital. Therefore, the valency of lithium is 1. Rubidium; Nitrogen -3; Calcium +2; Xenon; Mercury (use the periodic table included at the bottom of this to determine the order of the sublevels) 9. What is wrong with the following electron orbital diagram? What is the name of the rule that allows you to identify the error? 10. Problem Details. 9. Give the full electron configuration of a rubidium atom in the ground state. Provide the orbital diagram of the last subshell with electrons. Provide the quantum numbers for the last electron. Learn this topic by watching The Electron Configuration: Quantum Numbers Concept Videos. The orbital diagram for sulfur has seven boxes with two arrows pointing in opposite directions and two boxes with one arrow pointing up in each. The arrows. Energy levels: 2, 8, 6 Orbitals: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 If you need to fill in the little boxes, here's one for you. Each arrow represents one electron.
Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of rubidium-85 (atomic number: 37), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 37 protons (red) and 48 neutrons (orange). 37 electrons (white) include a relatively unstable electron in the outer shell (ring).
Orbital Filling Diagram Electron Configuration Electron Dot Diagram a. Boron b. Silicon c. Sulfur d. Calcium e. Iodine f. Rubidium g. Chromium h. Gallium Where are the Electrons? Write the full electron configuration, short-hand electron configuration, and fill in the orbital .
Rubidium (Rb) has an atomic mass of 37. Find out about its chemical and physical properties, states, energy, electrons, oxidation and more.
Rubidium (Rb) is the 37th element in the periodic table and its symbol is 'Rb'. The electron configuration of rubidium and the orbital diagram is the main topic in this article…. Potassium (K) electron configuration and orbital diagram Potassium (K) is the 19th element in the periodic table and its symbol is 'K'.
1. Write orbital filling diagrams, electron configurations, and electron dot diagrams for the following elements. Table: Element Orbital Filling Diagram Electron Configuration Electron Dot Diagram a. Boron b. Silicon c. Sulfur d. Calcium e. Iodine f. Rubidium g. Chromium h. Gallium
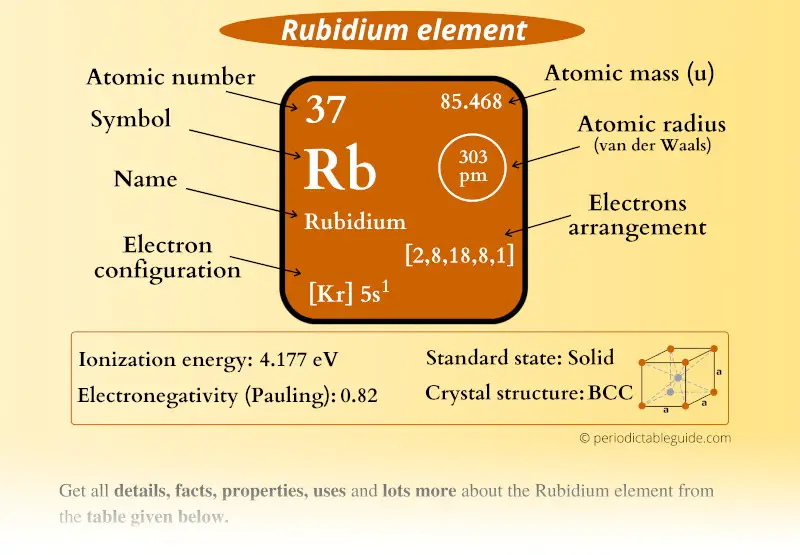
Rubidium electron configuration. Rb (Rubidium) is an element with position number 37 in the periodic table. Located in the V period. Melting point: 39 ℃. Density: 1.53 g/cm 3 . Electronic configuration of the Rubidium atom in ascending order of orbital energies: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 1.
Rubidium is no exception to this rule, being silvery-white and melting at 39 ºC. The element has two naturally occurring isotopes. Rubidium-85 is the dominant form, accounting for 72 per cent of the total, while most of the remainder is the radioactive rubidium-87, which has a half-life of 50 billion years.
Orbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration, showing the individual orbitals and the pairing arrangement of .. Rb+, Se2−. The first orbital (an s orbital) can contain only two electrons. . Rubidium. This diagram of a rubidium atom shows the electron shell.
Rubidium has an atomic number of 37, making it an alkali metal. This means that its last shell is an s with only one electron. The full notation is [Kr] 5s1.
Rubidium is an element (atomic number 37). What is the correct orbital diagram would be for the element nickel? Before you can make a diagram, you will need to know the atomic number. With the...
Orbital diagram of Rubidium (Rb) 38: Orbital diagram of Strontium (Sr) 39: Orbital diagram of Yttrium (Y) 40: Orbital diagram of Zirconium (Zr) 41: Orbital diagram of Niobium (Nb) 42: Orbital diagram of Molybdenum (Mo) 43: Orbital diagram of Technetium (Tc) 44: Orbital diagram of Ruthenium (Ru) 45:
Draw the orbital diagram for the following elements: Oxygen (O) Titanium (Ti) Silicon (Si) Copper (Cu) For each of the following elements, identify if the electron configuration is correct or incorrect. If it is incorrect, give the fix to the configuration. Carbon (C) = 1s22s22p2. Sulfur (S) = 1s22s22p63p6

/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)























Comments
Post a Comment