42 heteronuclear molecular orbital diagram
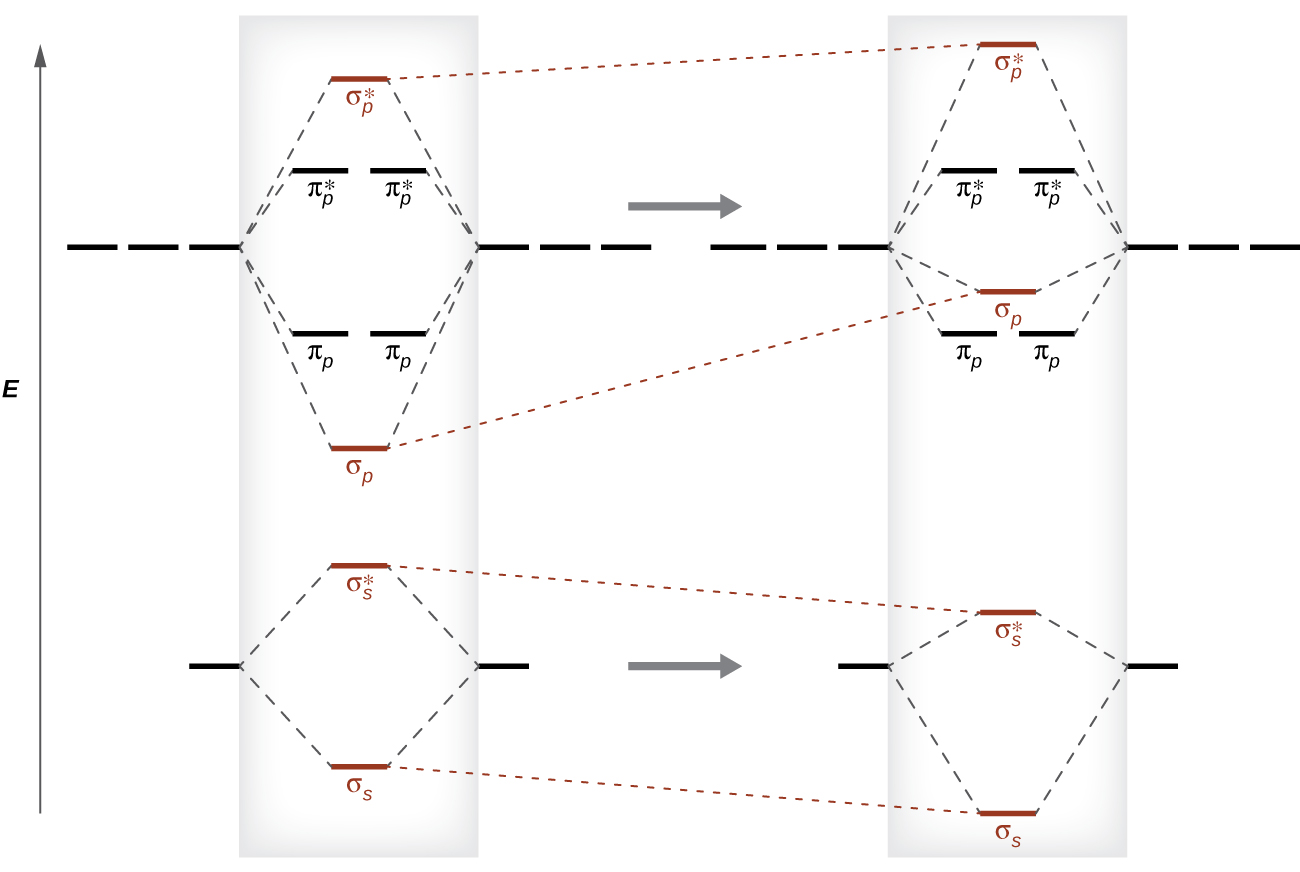
PDF MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in Molecular orbitals of heteronuclear diatomic molecules and ... By definition, electrons in nonbonding orbitals have no effect on bond order, so they are not counted in the calculation of bond order. Thus, the predicted bond order of HCl is (2 − 0) ÷ 2 = 1. Because the σ bonding molecular orbital is closer in energy to the Cl 3 p z than to the H 1 s atomic orbital, the electrons in the σ orbital are concentrated closer to the chlorine atom than to ...
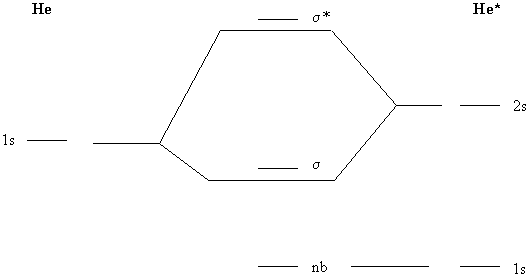
Heteronuclear Molecular orbital diagram - Summarized by Plex ... Jan 17, 2022 · In heteronuclear diatomic molecules, atomic orbitals only mix when the electronegativity values are similar. A s orbital on hydrogen could be involved in a molecular orbital picture of HF, as seen by a s orbital on fluorine in a molecular orbital picture of HF.
Heteronuclear molecular orbital diagram
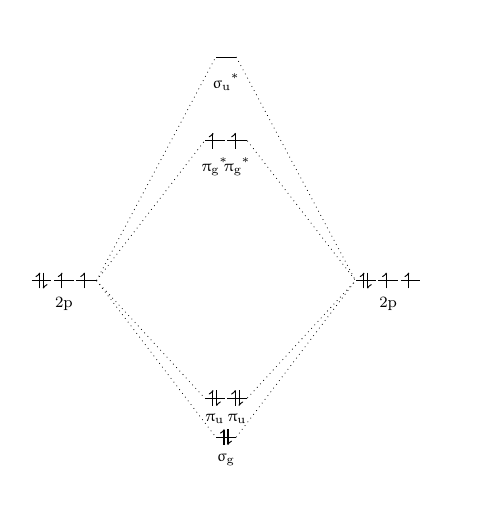
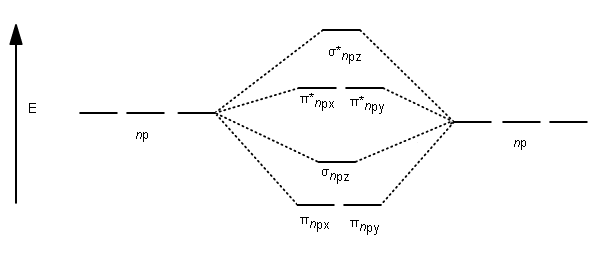
Molecular Orbitals of Heteronuclear Diatomics Molecular Orbitals of Heteronuclear Diatomics The molecular orbitals of heteronuclear diatomics (HF, CO, CN-, etc.) can be predicted using the same principles that we used to construct the molecular orbitals of homonuclear diatomics: i) Ignore the core electrons ii) Remember that the total number of MOs = total number of AOs Difference Between Homonuclear and Heteronuclear Diatomic ... Key Difference - Homonuclear vs Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Diatomic molecules are substances composed of two atoms per molecule. These molecules are composed of two atoms bonded to each other via covalent chemical bonds.The atoms can be bonded via single bonds, double bonds or triple bonds. Depending on the types of atoms present in the diatomic molecule, there are two types of ... Comparing Homonuclear and Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules ... Students first learn the basics of WebMO by building and optimizing 2 small molecules. They then calculate and visualize the molecular orbitals of two diatomic molecules (N 2 and BF) and observe how going from a homonuclear to heteronuclear molecule changes the shape of different molecular orbitals.. As written this activity uses the WebMO demo server so no computational chemistry software ...
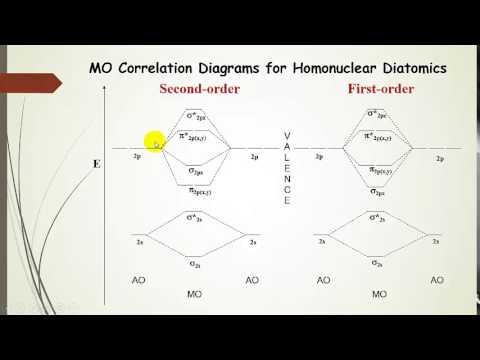
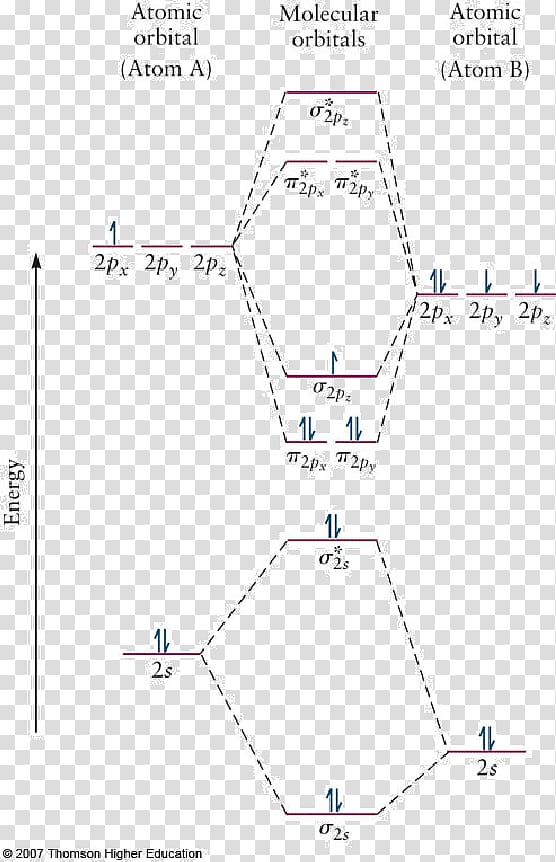
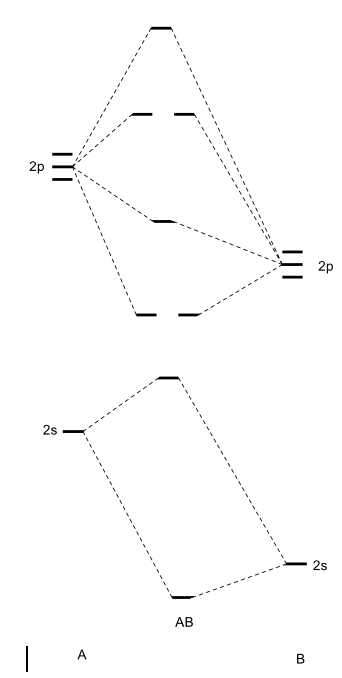
Heteronuclear molecular orbital diagram. 5.3: Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules - Chemistry LibreTexts 5.3: Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules. Diatomic molecules with two non-identical atoms are called heteronuclear diatomic molecules. When atoms are not identical, the molecule forms by combining atomic orbitals of unequal energies. The result is a polar bond in which atomic orbitals contribute unevenly to each molecular orbital. PDF The molecular orbital - Darbhanga College of Engineering 2. Individual atomic orbitals (AO) are arranged on the far left and far right of the diagram. 3. Overlapping atomic orbitals produce molecular orbitals located in the middle of the diagram. These MO overlap with either a sigma or pi bond and are designated in bonding, nonbonding, or antibonding orbitals with respect to their phases. 4. MO Theory: Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules - Chemistry ... Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Heteronuclear Diatomics. Concept #1: Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Heteronuclear Diatomics ... Report issue. Example #1: Construct the Molecular Orbital Diagram for carbon monoxide, CO. Report issue. Practice: Apply Molecular Orbital Theory to determine the MO orbital diagram for the CF + ion. 03 Molecular Orbitals of Heteronuclear Diatomics | Susan Findlay Exercise 3.2: Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Heteronuclear Diatomics (Answers) 173 KB: Exercise 3.3: Bonding vs. Antibonding vs. Nonbonding: 206 KB: Exercise 3.3: Bonding vs. Antibonding vs. Nonbonding (Answers) 29 KB: Practice Test Questions 3: Molecular Orbitals of Heteronuclear Diatomics: 111 KB
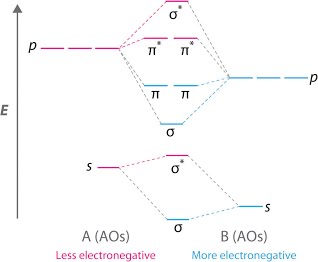
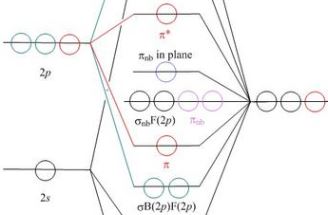
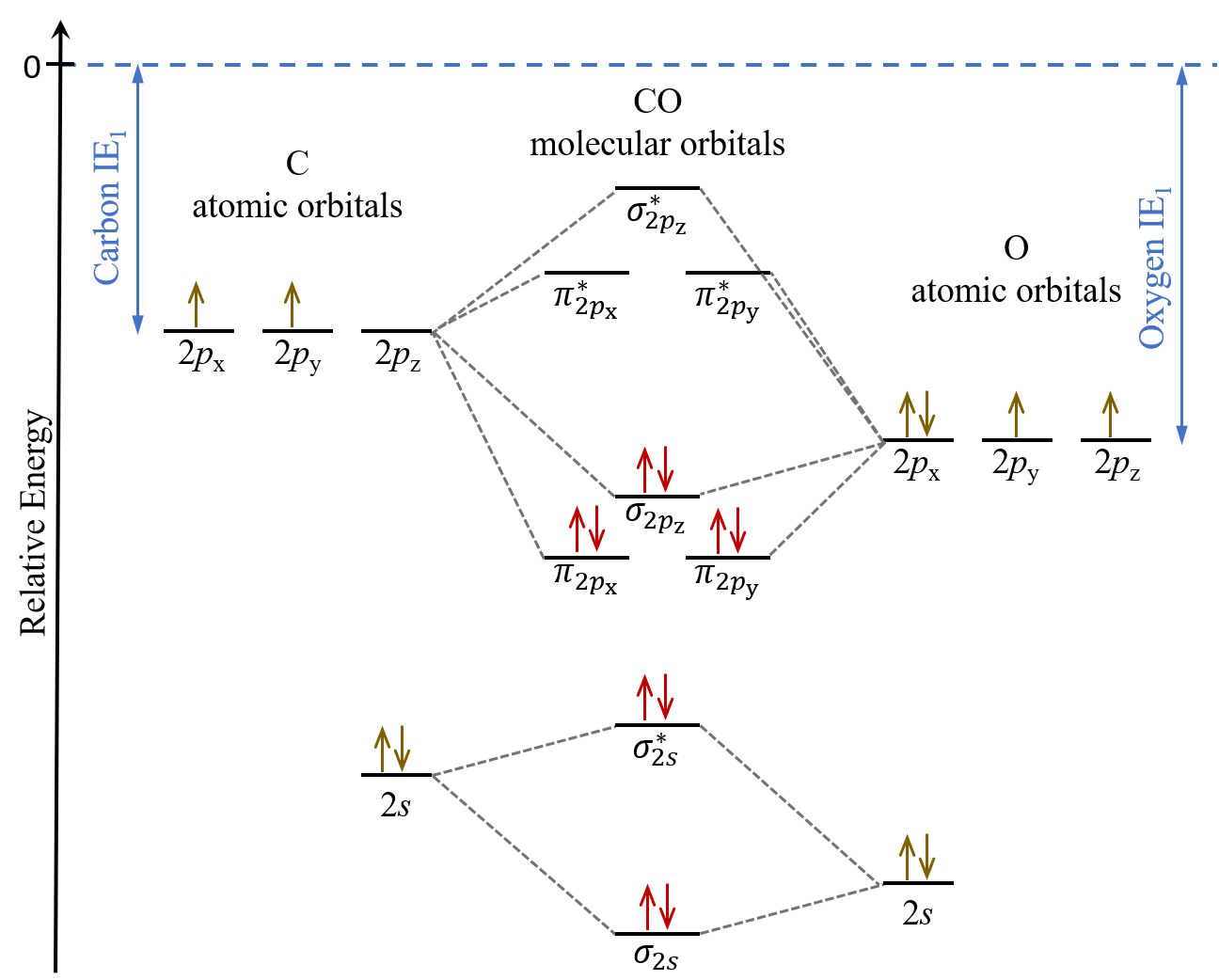
Energy level of molecular orbitals in heteronuclear ... If we look at the molecular orbital diagram for carbon monoxide, you are right, the bonding pi orbitals are lower in energy than the bonding sigma orbital: The reason for this is due to the contributions from carbon. This comes from the relative energies of the atomic orbitals. ... Molecular orbitals of heteronuclear diatomic molecules. Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules - CHEMISTRY COMMUNITY Re: Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules. Electronegativity is the electron pulling power of an atom, and an atom with a higher electronegativity will pull the shared electrons pair more towards itself. This is true for bonding orbitals, where the more electronegative atom will dominate. However, this is not true for antibonding orbitals. Molecular Orbitals - Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear ... Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Molecules. The molecular orbitals which describe the motion of a single electron in a molecule containing two unequal nuclear charges will not exhibit the g and u symmetry properties of the homonuclear diatomic case. The molecular orbitals in the heteronuclear case will in general be concentrated more around one nucleus than the other. inorganic chemistry - Molecular orbitals of heteronuclear ... Energy level of molecular orbitals in heteronuclear diatomic compounds. Related. 3. Molecular orbitals and "generalized" aufbau principle for heteronuclear molecular configurations. 1. How to compare the energies of sigma and pi bonds in molecular orbitals of diatomic heteronuclear species? 2.
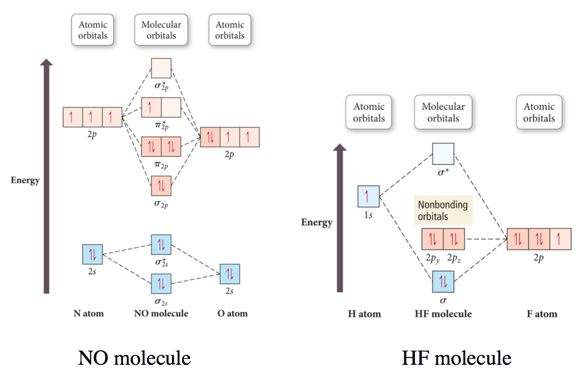
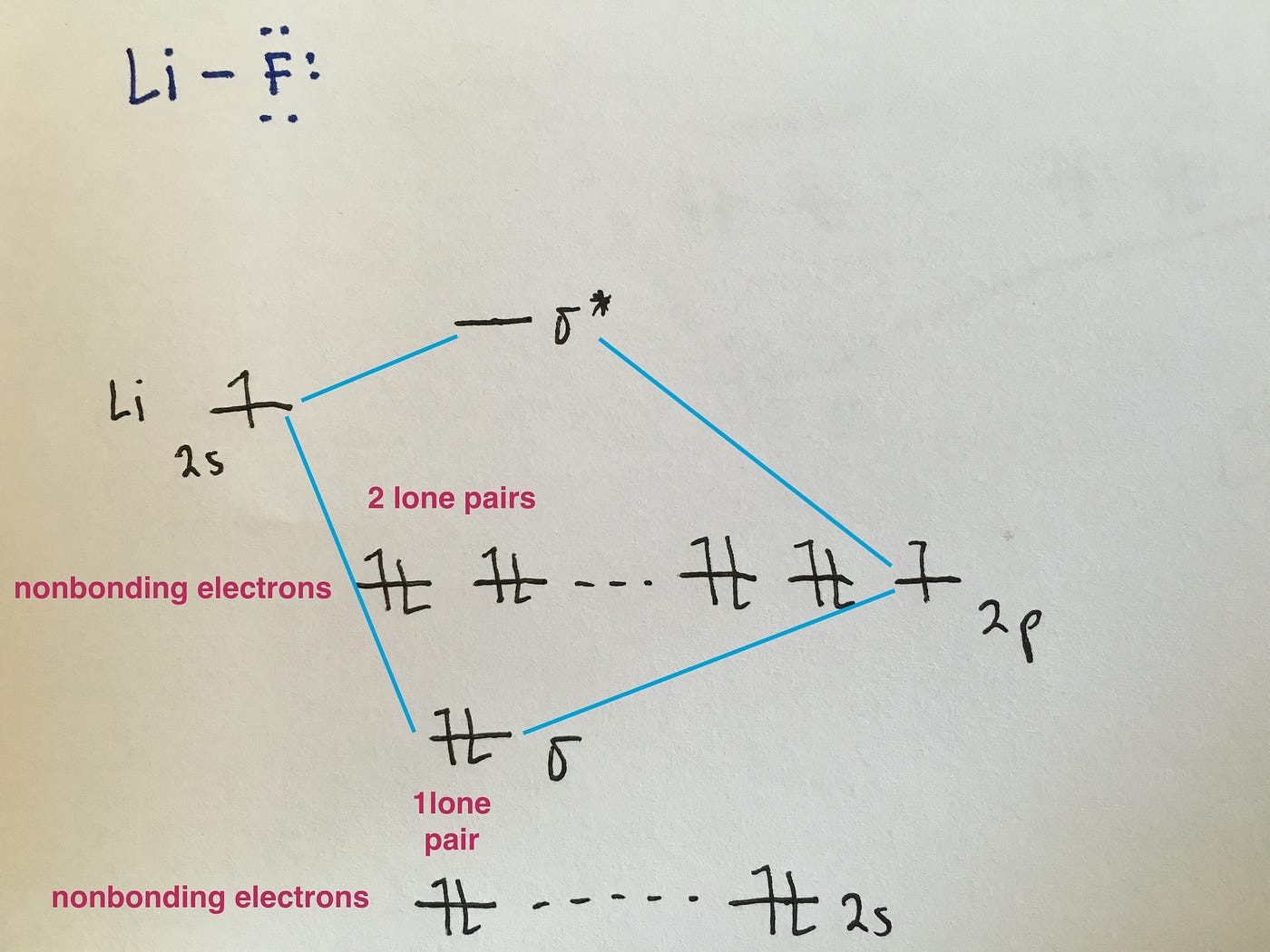
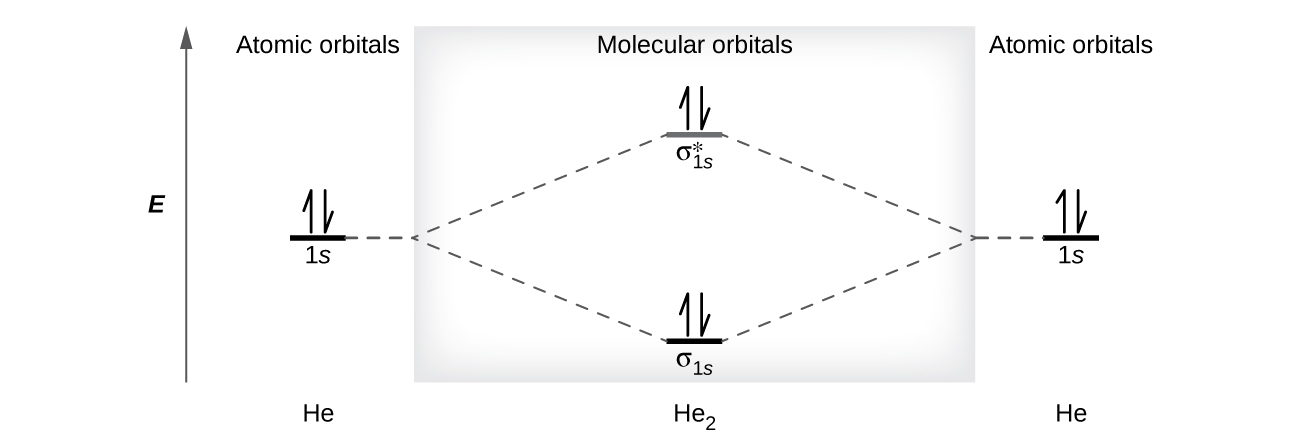
How do you use molecular orbital diagrams? Nitric oxide is a heteronuclear molecule that exhibits mixing. The construction of its MO diagram is the same as for the homonuclear molecules. It has a bond order of 2.5 and is a paramagnetic molecule. The energy differences of the 2s orbitals are different enough that each produces its own non-bonding σ orbitals. What is the bond order of the heteronuclear diatomic ... What is the bond order of the heteronuclear diatomic molecule no? Because 10 electrons are sufficient to fill all the bonding molecular orbitals derived from 2p atomic orbitals, the 11th electron must occupy one of the degenerate π * orbitals. The predicted bond order for NO is therefore (8-3) ÷ 2 = 2 1/2 . Click to see full answer. Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules | Introduction to Chemistry Examples of Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules. In hydrogen fluoride, HF, symmetry allows for overlap between the H 1s and F 2s orbitals, but the difference in energy between the two atomic orbitals prevents them from interacting to create a molecular orbital. Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A heteronuclear diatomic molecule is composed of two atoms of two different elements. Examples include CO, HCl, and NO . Dihydrogen H2 Molecular Orbital Diagram MO diagram of dihydrogen Bond breaking in MO diagram The smallest molecule, hydrogen gas exists as dihydrogen (H-H) with a single covalent bond between two hydrogen atoms.
Bioprofe | Chemistry | Molecular Orbital Theory This method, called molecular orbital theory, begins with a simple description of the molecules, but quickly becomes complex in the details. Theory assigns the electrons of a molecule to a series of orbitals that belong to the complete molecule, which are the so-called molecular orbitals. In the same way as atomic orbitals, molecular orbitals ...
Solved Molecular orbitals of heteronuclear diatomic ... Transcribed image text: Molecular orbitals of heteronuclear diatomic molecules (21 points). Refer to the to orbital diagram for hydrogen fluoride (HF) to answer questions a through d below HF MOS 40* 1π 2a a. Add electrons to the diagram to indicate the ground-state electron configuration of HF b.
Molecular orbital theory. Heteronuclear diatomics. CO ... 12-12 This video describes the molecular orbital theory diagram of CO, placing emphasis on how MO theory differs for homo and heteronuclear diatomics
Heteronuclear Molecules Frontier Orbitals • Many properties of molecules can be interpreted through the use of the molecular orbital model, and in particular by looking at the frontier orbitals: – the HOMO (highest occupied molecular orbital) –> Donor orbital – the LUMO (lowest unoccupied molecular orbital) –> Acceptor orbital
MO Diagram for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules ... Re: MO Diagram for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules [ENDORSED] We label a molecular orbital "sigma 2s" only when it correlates to two atomic 2s orbitals. With molecular orbitals that correlate to more than one type of atomic orbital, we have to use an alternative notation, where each set of molecular orbitals of a certain type (sigma, pi) is ...
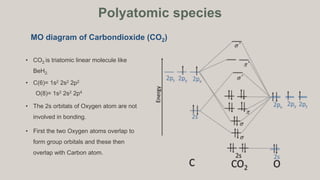
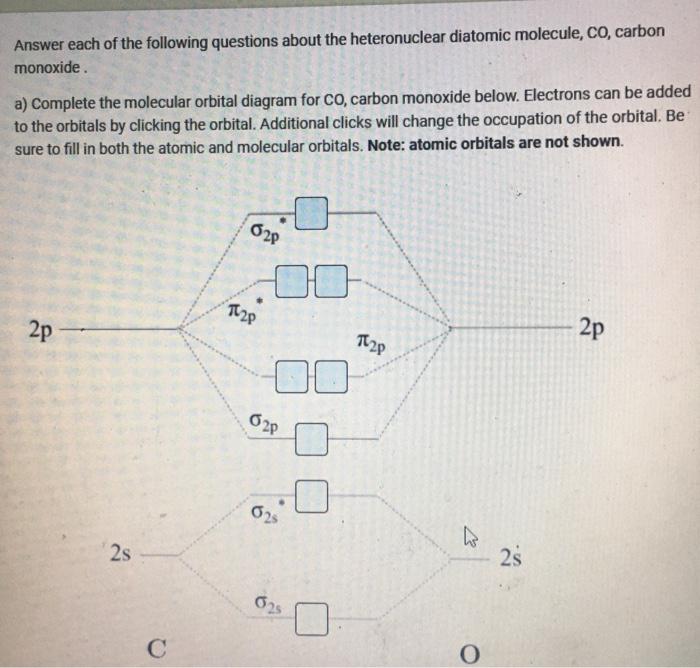
D6.5 MOs for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules – Chemistry 109 ... Diatomic molecules with two non-identical atoms are called heteronuclear diatomic molecules, examples include CO, NO and HCl. Molecular orbital diagrams for these molecules have one more layer of complexity, but they also serve to explain many bond and molecular properties we will encounter later on in the course. Let’s consider CO as an example.
High-order-harmonic generation in homonuclear and ... 2) and heteronuclear (CO, BF, and HF) molecules in intense ultrashort laser pulses with the emphasis on the role of multiple molecular orbitals (MOs). The results reveal intriguing and substantially different nonlinear optical response behaviors for homonuclear and heteronuclear molecules.
8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams — Flux Science 8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams. Abstract (TL;DR) Molecular orbital diagrams are a fantastic way of visualizing how molecular orbitals form using what we already understand about sigma and pi bonds. Depending on if it is a homonuclear case, where the bonding atoms are the same, or a heteronuclear case, where the bonding atoms are ...
What is molecular orbital diagram of CO? - handlebar ... What is molecular orbital diagram of CO? Carbon monoxide MO diagram. Carbon monoxide is an example of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule where both atoms are second-row elements. The valence molecular orbitals in both atoms are the 2s and 2p orbitals. The molecular orbital diagram for carbon monoxide (Figure 5.3. Is there SP mixing in CO?
Solved Question 7 3 points Save A Draw the molecular ... Question 7 3 points Save A Draw the molecular orbital diagram (MO diagram) for the heteronuclear diatomic species CF to answer the following questions. Only show the valence Atomic orbitals and valence Molecular orbitals. The order of MO energy levels for CF will be the same as for the O2 homonuclear diatomic molecule.
Molecular Orbital Theory for Heteronuclear Diatomic ... Dr. Shields explains how to apply Molecular Orbital Theory to heteronuclear diatomic molecules. Differences in electronegativity between the two atoms in th...
Comparing Homonuclear and Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules ... Students first learn the basics of WebMO by building and optimizing 2 small molecules. They then calculate and visualize the molecular orbitals of two diatomic molecules (N 2 and BF) and observe how going from a homonuclear to heteronuclear molecule changes the shape of different molecular orbitals.. As written this activity uses the WebMO demo server so no computational chemistry software ...
Difference Between Homonuclear and Heteronuclear Diatomic ... Key Difference - Homonuclear vs Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Diatomic molecules are substances composed of two atoms per molecule. These molecules are composed of two atoms bonded to each other via covalent chemical bonds.The atoms can be bonded via single bonds, double bonds or triple bonds. Depending on the types of atoms present in the diatomic molecule, there are two types of ...
Molecular Orbitals of Heteronuclear Diatomics Molecular Orbitals of Heteronuclear Diatomics The molecular orbitals of heteronuclear diatomics (HF, CO, CN-, etc.) can be predicted using the same principles that we used to construct the molecular orbitals of homonuclear diatomics: i) Ignore the core electrons ii) Remember that the total number of MOs = total number of AOs













Comments
Post a Comment